The Baumol Model in 1952 considers cash management complication as same to inventory management problem. For itself the firm attempts to minimize the total cost that is the sum of cost of holding cash and the transaction cost or cost of converting marketable securities to cash. The Baumol model is depends on the subsequent assumptions as:
- The firm is capable to forecast its cash require with certainty,
- The opportunity cost of holding cash is identified and it does not modify over time, and
- The transaction cost is not change.
Let us suppose that the firm sells securities and begins with a cash balance of C rupees. Over a period of time this cash balance reduces steadily and attains zero. At that point the firm replenishes its cash balance to C rupees through selling marketable securities. Such pattern continues over an era of time. Because the cash balance decreases steadily thus the average cash balance is C/2. Such type of pattern is demonstrated in figure 3.
Cash Balance
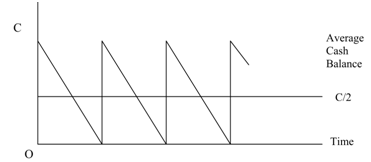
Figure: Pattern of Cash Balance: Baumol's Model
The firm incurs a holding cost for keeping cash balance. This is an opportunity cost that is the return foregone on market-able securities. The firm's holding cost for maintaining an average cash balance is as given below, whether the opportunity cost is I:
Holding Cost = I (C/2).
The firm incurs a transaction cost when this converts its marketable securities to cash. Total number of transactions throughout the year would be the total fund need T divided via the cash balance C that is T/C. Because per transaction cost is assumed to be constant and whether per transaction cost is B the net transaction cost would be as B (T/C).
The total cost may be appears as: TC = I (C/2) + B (T/C)
= Holding cost + Transaction cost
Here
C = Amount of marketable securities converted into cash per cycle
I = Interest rate earned on marketable securities
T = Projected cash requirement during the period
TC = Total cost or sum of conversion and holding costs.
The value of C that minimizes TC may be determined from the subsequent equation:
C* =√(2bt/I)
The above equation is derived as given below:
Determine the first derivative of total cost function regarding C.
dTC/dC = ((I/2) - (bT/c2))
Setting the first derivative equivalent to zero, we acquire
((T/2) - (bT/ c2)) = 0
Solving for C as
C* =√(2bt/I)
One can confirm for second derivative condition ensuring that C* to be minimized.