Molecular Structure
The polymers have three distinct arrangements of molecular chain, hence resulting in three structures.
In amorphous structure the molecular chain are arbitrarily arranged and bent various times. These chains, as demonstrated in following figure (a), cannot move easily past each other due to their entangled nature. Thermosetting plastics have merely this structure and contain higher strength because entangled chains needs high stress for their displacement. They need higher temperature also for straightening of chains. Various thermoplastics also have amorphous structure.
A crystalline structure in polymers needs all the chains to be aligned in single direction as depicted in following figure (b). The geometrical regularity in polythene, shown in above figure (c) of POLYMERISATION, is the illustration of crystalline polymer. The symmetry of chains or macromolecules is lost due to attachment of bulky molecule to randomly available bonds in the chain. Polyvinyl acetate demonstrated in figure of Co-polymerisation of Vinylchloride or C2H3Cl and Vinylacetate or OCOCH3, is an instance of amorphous structure.
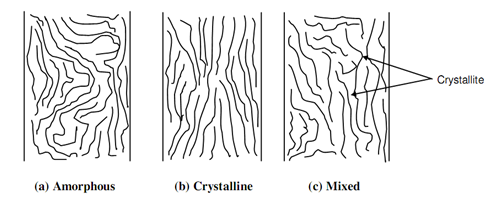
In specific cases the entire structure may be in groups of amorphous and crystalline macromolecules. That mixed structure is demonstrated in above figure (c). The region where chains are crystalline or aligned is termed as crystallite.
Separately from basic chemical nature, polymer properties are affected via its structure. The chain molecules exhibit strength along their length only if chain molecules produce oils or soft solids as paraffin. The polymer molecular weights controlled by weight fraction of constituents and chain length also. Those polymers that have higher molecular weight are more heat resistant and tough. The gummy and soft are low density polymers. The long chain molecules can be cross-linked via introducing those polar groups as carboxyl, hydroxyl, chlorin, nitrite or flurorin. Such cross-linking will raise secondary inter macromolecular forces and so overall strength and inflexibility.
Dense crystalline structure offers high melting point that is sharply defined, high tensile density and strength as compared to amorphous polymer. For the same purpose these materials are brittle. Their impact strength and flexibility may be enhanced by initiated amorphous characteristic in the structure. Copolymerisation is one manner of reducing symmetry and raising flexibility. Copolymer of vinylacetate and vinylchloride termed as polyvinylacetate as presented in figure of Co-polymerisation of Vinylchloride (C2H3 Cl) and Vinylacetate (OCOCH3,) is the instance of improvement in flexibility.
Crystalline polymers Flexibility is also increased via addition of several substances called plasticiser. Three common plasticisers are as:
- non-drying vegetable oils,
- monomeric chemical of high boiling point temperature, and
- Polymeric resinous material of low molecular weight.
These plasticisers contain positions among the molecular chains whereby the force of attraction among them reduces. This allows them to move relative to each other and thus flexibility enhances. Though, the tensile strength will decrease.