Model without Stock Effects
In this model it is assumed that extraction cost depends only on extracted quantity. Let us assume that St is the remaining stock of natural resource at time t, Et is the quantity of extraction, Pt is the price at which it is sold in the market, r is the discount rate and C(Et) is the total cost of extraction. The problem before us is
Equation 1
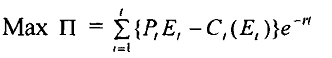
Here we consider the time period t = 1 .... T.
Total profit is ∏, which is the sum of 'revenues minus costs' during all time periods under consideration.
When we extract Et in time period’t’ there is depletion to the stock. Therefore,
Equation 2
St = St-1- Et for all t.
In addition, final stock that remains cannot be negative. Thus, we impose the constraint
ST > 0
The Lagrangian function for the above problem is given by
Equation 3
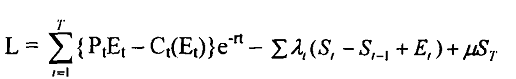
On solving equation 3 the first order condition yields
Equation 4
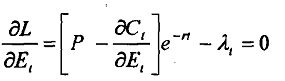
As you know Quantitative Methods, λ, in equation 4 is the present value of the shadow price or opportunity cost, and
Equation 5
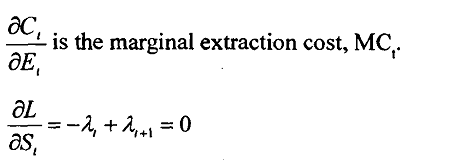
Equation 6

An implication of the first order condition equation 5 is that λt = λt=1 for all t, which means the present value of shadow price is constant over time, or it is time independent.
Let us denote 'resource rent' or royalty to be paid as Rt which is given by
Rt= Pt - MCt = λtert from the first order condition.
It can be easily shown that
Equation 7
Rt = λtert and Rt / Rt = r
Where dot over a variable represents its derivative, i.e., instantaneous change in it. Thus R denotes the change in R, i.e., resource rent. From equation 7 we find that resource rent rises at the rate ‘r’. The resource rent is equivalent to the present value of opportunity cost. Hence, the present value of opportunity cost rises at the rate equal to market rate of interest (which we had taken as our discount rate).
The model presented at equation 1 can be expressed using discreet time variable.
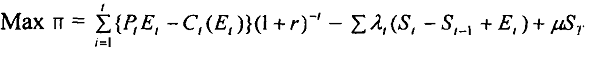
The first order condition would yield
Equation 8
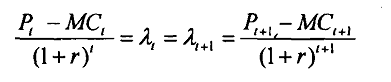
By rearranging terms in equation 8 it is easy to show that
Equation 9
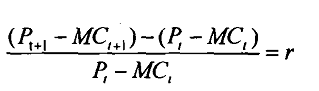
This yields the same result that the resource rent increases at the rate 'r' over time. Moreover,
Equation 10
Pt =MCt + λt (1+r)t
Equation 10 shows that optimal extraction rate is the one at which the sum of marginal cost and the current value opportunity cost is equal to price.
μ = λT = constant If ST > 0 then λ= 0
If ST = 0 then λ > 0
Opportunity cost is positive only if the resource stock is completely exhausted within the time horizon.
The following results are popularly known as Hotelling's Lemma.
(i) Current value opportunity cost increases at the constant rate 'r' equal to market rate of interest.
(ii) Present value of opportunity cost is constant over time.