MinMax Search
Parents frequently get two children to share a cake by asking one to cut the cake and the other to select which half they want to eat. In this two player cake-scoffing game, in only one move (cutting the cake) player one soon learns that if he wants to maximize the amount of cake he gets, he had to cut the cake into equal halves, because his enemy is going to try and minimize the cake that player 1 gets by selecting the biggest half for her.
Imagine we have a two player game where the winner scores a positive number at the end, and the loser scores nothing. In board games such as chess, the score is normally just 1 for a win and 0 for a loss. However, in other games such as poker one player wins the (cash) amount that the other player loses. These all are called zero- sum games because when you add one player's winnings to the other player's loss the sum is zero.
The minima algorithm is called because it assumes that you and your opponent will be act rationally, and so you will select moves to try to maximise your final score and your opponent will choose moves to try to minimise your final score. It is helpful to have a game where the search tree is small to demonstrate the minima algorithm. This is the reason for invent the following very trivial game:
Take a pack of cards and deal out 4 cards face up. 2 players take it in turn to select a card each until they have 2 each. The object is to select 2 cards so that they add to an even number. The winner is the one with the biggest even number n (picture cards all count as 10), and the winner scores n. If both of the players get the same even number, it is a draw and both score are zero.
Imagine the cards dealt are 3, 7,5 and 8. One should choose first in which card player he has interest and the minima algorithm can be used to decide this . To demonstrate this, we will draw the whole search tree and put the scores below the final nodes on paths which represent particular games.
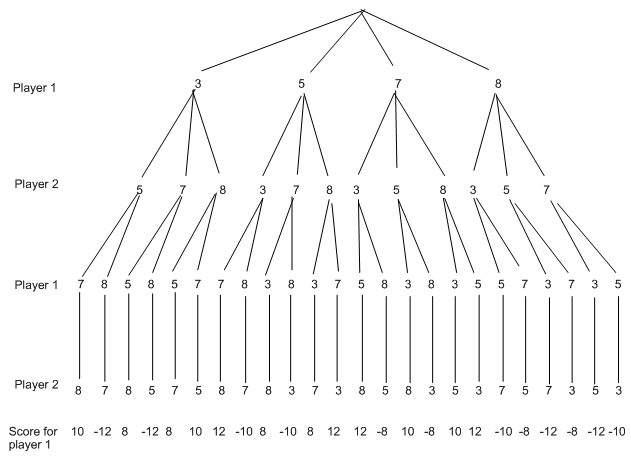
Our goal is to write the best score on the top branches of the tree that player one can guarantee to score if he chooses that move. To do this in the starting at the bottom, we will write the concluding scores on successively higher branches on the search tree until we reach on the top. Whenever there is a option of scores to write on a specific branch, we will assume that player 2 will choose the card which minimises player one's final score, and player 1 will select the card which maximises his/her score. Our aim is to move the scores all the way up the graph to the top, which will make possible for player one to choose the card which leads to the best guaranteed score for the overall game. We will initial write the scores on the edges of the tree in the bottom two branches
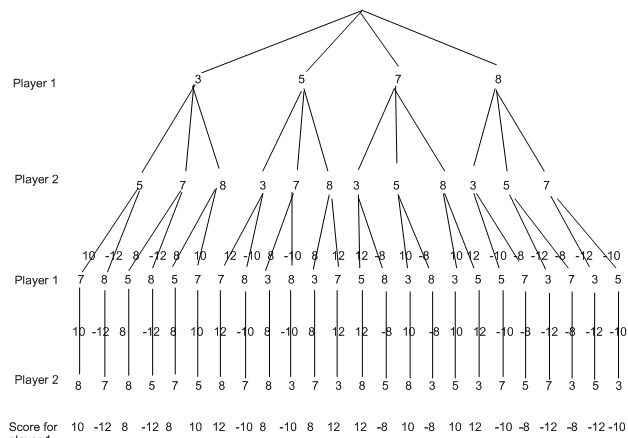
We want to move now the scores up to the next level of branches in the tree. But there is a option. For example, for the first branch on the second row, we could write either 10 or 12. This is where our assumption regarding rationality comes into concern. We should write 10 there because imagine what player 2 has in fact chosen the 5, and then player 1 can choose either 7 or 8. Selecting 7 would result in a score of 10 for player 1, selecting 8 would result 12. Obviously player 1 would select the 7, thus the score we write on this branch is 10. Hence, we should select the maximum of the scores to write on the edges in the row above. we get the following by doing the same for all the other branches:
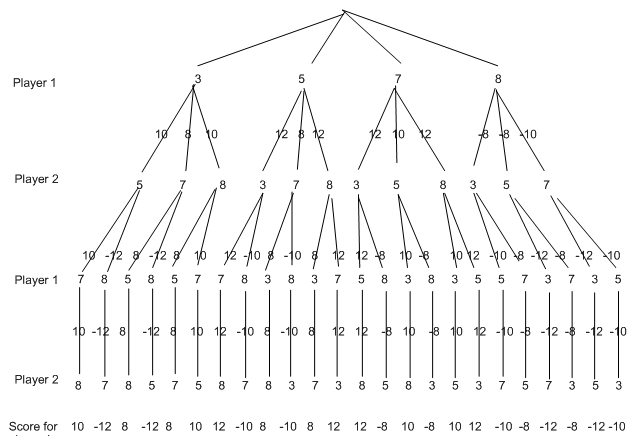
In the final we want to put the scores on the top edges in the tree. there is a choice again . In this type of case, however, we have to remember that player 2 is making the selection, and they will act in order to minimise the score that player 1 gets. Thus, in this case when player 1 chooses the 3 card, player 2 will choose the 7 to minimise the score player 1 can obtain. Hence, we select the minimum possibility of the 3 to put on the edges at the top of the tree as follows:
To select the right first card, player 1 simply looks at the topmost edges of the final tree and select the one with the highest score. selecting the 7 ,In this case, will guarantee player 1 scores 10 in this game (assuming that player one select according to the minima method for move 2 but-essentially - making no assumptions about how player 2 will choose).
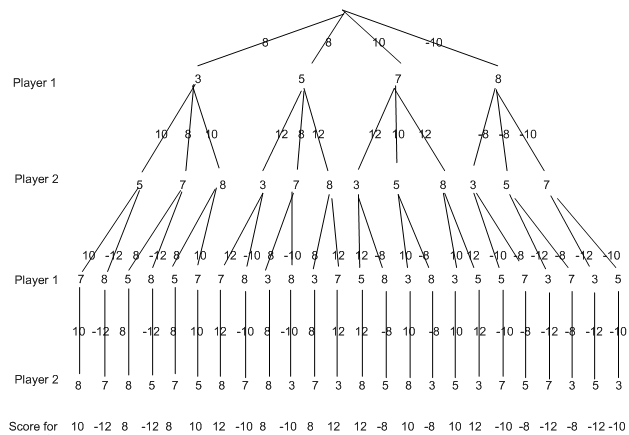
Notice the above process was in order for player 1 to choose his/her first move. The complete process would need to be repeated again and again for player two's first move, and player one's second move, and so on . Agents playing games, in general, using a minimax search have to calculate the best move at every particular stage using a new minimax search. Donot forget that only because an agent thinks their opponent will act rationally, doesn't mean they will act rationally, thus they cannot assume a player will make a specific move until they have actually done it.