The Milky Way Galaxy:
The white band stretched across the night sky is, in fact, a partial view of the Milky Way Galaxy. Being inside the Galaxy, we can see it only in parts. We cannot see the whole of it, the way we see the other galaxies. Visualising the whole Milky Way Galaxy and determining its shape has not been easy. By watching a large number of galaxies distributed in all directions in dozens of views as far as modem telescopes can see, scientists have been able to form a picture of what our galaxy must look like from outside. In ihis, they have also been helped by the observations about the stars in our galaxy, their distances and motion, etc. The picture of the Galaxy constructed by the astronomers is shown in Fig. Doesn't it look somewhat like a disc or a gramophone record with a swollen centre? The Milky Way Galaxy contains about 100 billion stars. The stars are not uniformly distributed. You can test this yourself by a simple activity.
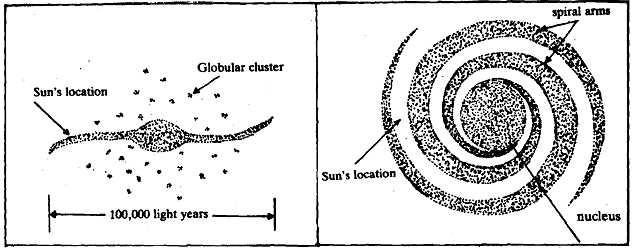
concentration of stars in certain parts of the sky. There is a great concentration of stars towards the centre of the Galaxy, which is located in the constellation of Sagittarius. The Sun is.situated on its remote outskirts, about 30,000 light years away from the centre. Note that when you see the portion of the Milky Way in the sky near Sagittarius, you would be looking toward the centre of the galaxy. When you observe the portion near Orion, you would be seeing the "edge" of the Galaxy, nearest the Sun. The Galaxy, as you can sec in Fig. 9.8, is disc shaped. If we could see our galaxy from the top, we would get the face-on view (Fig. ). If we could see it from the edge, we would get the edge-on view (Fig.). In the edge-on view, the Galaxy consists of two basic parts: the disc and the halo. The disc consists of stars, as well as clouds of gas and dust called nebulae. It has a diameter of 100,000 light years, and a thickness of about 5,000 light years. This collection of gas and stars rotates about the centre (also known as the nucleus) of the Galaxy, with each part moving at a different speed. The Solar System at a distance of about 30,000 light years from the centre, in the outskirts of the Galaxy, also revolves. Moving at a speed of 250 km per sec., it takes roughly 200 million years to complete one revolution around the centre of the Galaxy. There are individual stars like the Sun as well as groups of stars, called galactic clusters, that move together in the disc. Astronomers have identified about 1000 galactic clusters in the disc, each containing 10 to 1,000 stars.