MECHANISM OF FERTILIZATION -
The process of fertilization complete into 5 steps -
1. APPROACH OF SPERM TO OVUM
- For fertilization sperm & ova interaction is essential.
- Sperm are motile, sperm reach to the ovum, with the help of tail movement but it is a chance.
- In animal which exhibit internal fertilization, the sperms are deposited close to the fertilization site with the help of copulatory organ. In many animals the ovulation take place after copulation.
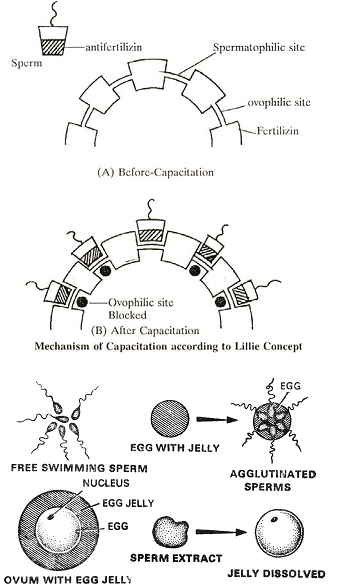
2. CAPACITATION AND CONTACT -
- Capacitation is a type of chemotaxis process.
- Fertilization is a specific process & it takes place in the gametes of same species.
- Lillie (1919) proposed the fertilization theory.
LILLIE THEORY -
- According to it, there is a substance called fertilizin on the ovum surface which is a glyco-protein. It is different in different species.
- Anti-fertilizin present on the surface of sperms. It is a simple acidic protein.
- It is attached to the proteins of sperm plamalemma. Fertilizin & anti-fertilizin react like antigen antibody.
- As a result the sperms get attached to ovum surface. It is called as sperm agglutination.
- The fertilizin & anti-fertilizin of the same species can react. Hence, sperms identify the ovum of same species.
- The vitelline membrane of the ovum has many binding receptor sites which react with the binding protein of the sperms.
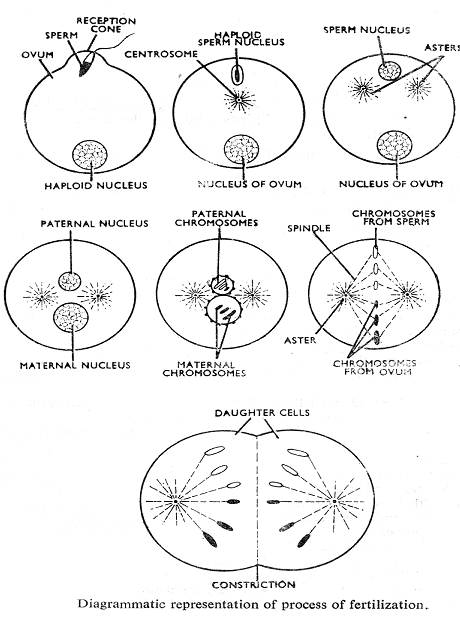
3. ACROSOME REACTION & PENETRATION -
- This reaction take place after the attachment of the sperm to the egg surface.
- There are specific changes in the acrosome region which are collectively called as acrosomal reaction.
- According to colwin & colwin, the acrosome first elongates to form an acrosomal tubule.
- The length of the acrosomal tubule varies from species to species.
- Normally its length is double than the length of the nucleus.
- The sperm with acrosomal tubule is called as active sperm.
- The acrosomal tubule release sperm lysins eg. hyaluronidase enzyme in mammals.
- The sperm lysins digest egg membranes to create a passage for sperm entry.
- Finally, there is a contact between the plasmalemma of both sperm & ovum.
4. ACTIVATION OF EGG -
- When acrosomal membrane contract to plasmalemma of ova, these membranes are fused.
- During this period many changes take place in the ooplasm, these changes are collectively called activation of egg.
- It involves -
(i) Colour change -
- Surface of egg white (previously yellow) due to distribution of fat, equally after the contact of sperm.
- Colour changes initiate to contact site of sperm.
(ii) Formtion of fertilization cone -
- The ooplasm at the point of contact of sperm bulges out to form a reception cone or fertilization cone.
- The fertilization cone may be provided with pseudopodia -like or cylendrical processes.
- The fertilization cone gradually engulfs the sperm & get withdrawn.
- The fertilization cone is also called as receptor cone.
- In ova, nucleus of sperm, periacrosomal material, proximal centriole and mitochondria are enter.
(iii) Cortical reaction and formation of fertilization membrane -
- After the entry of the sperm into the ova so many changes in the ooplasm. These changes are physio-chemical type, which are collectively called as cortical reaction.
- There are cortical granules just below the plasmalemma which are made up mucopolysaccharides.
- These cortical granules release mucopolysaccharides into the perivitelline space.
- The perivitelline space is found between the plasmalemma of ovum & vitelline membrane.
- These mucopolysaccharides fuse with the vitelline membrane & form a fertilization membrane.
- The fertilization membrane prevents the further entry of the sperm.
(iv) Metabolic activation -
Entry of sperm into the ovum stimulates many metabolic changes which are as follows -
(a) The permeability of plasmalemms for water, ethylene glycol, phosphate, potassium is increased.
(b) Beginning of synthesis of cAMP which inturn stimulates other metabolic activities.
(c) Activation of ETS to form ATP.
(d) Beginning of protein synthesis with the help of mRNA & other RNA.
(e) The rate of O2 consumption is changed. For example, it increase in the eggs of sea urchin, decreases in molluscs & chaetopterus & remain unchanged in Bufo.
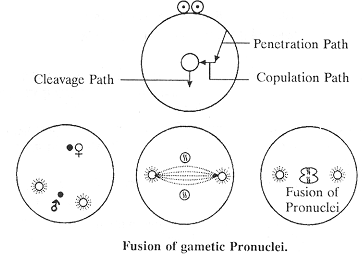
5. FUSSION OF GAMETIC PRONUCLEI -
- The nuclei of both ovum & sperm absorb water and they swell to become vesicular or jelly-like. Such nuclei are termed as pronuclei.
- Simultaneously, the sperm rotates to 180° so that the mid-piece assumes the leading position.
- The male pronuclei moves towards the female pronuclei.
- The path of the movement of male pronuclei is called as fertilization path or copulation path.
- Both the pronuclei fuse to form zygote which is called as amphimixis.
- Amphimixis take place in the centre of the yolk free ooplasm.
- Entry way of sperm in the ova is called as penetration path.
- Zygote move toward the one specific site, this way is called cleavage path.