MECHANISM -
1. AURICULAR SYSTOLE -
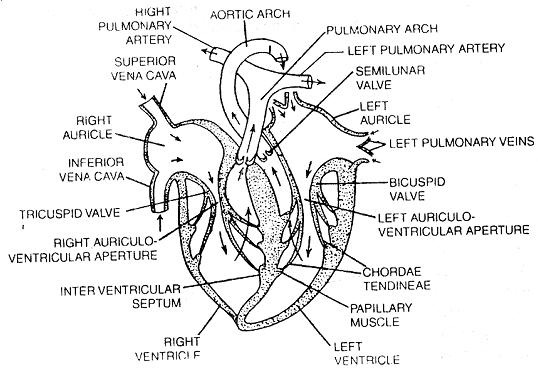
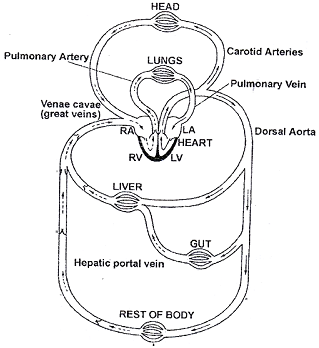
First of all from complete body impure blood comes in R.A. by superior and inferior vena cava or pre and post cavals.
Pure blood comes in L.A. by pulmonary veins.
Both auricles contract, so their blood comes in respective ventricles by tricuspid and bicuspid valve.
2. VENTRICULAR SYSTOLE -
Both ventricles contract.
Tricuspid & bicuspid valves are closed.
First sound of lubb is heard which is slow and for long time.
Blood enters into pulmonary aorta and carotico systemic arch, so semilunar valves are closed, second sound of dup is heard which is loud and for short period.
Cardiac out put depends on coming out of blood from L.V. only.
3. HEART DIASTOLE -
Volume of heart starts to increase.
By sucking pressure blood comes in auricles by veins.
4. HEART BEAT -
The spontaneous and rhythmic contraction & relaxation of heart to pump out and receive blood is called heart beat.
So systole and diastole are collectively known as heart beat.
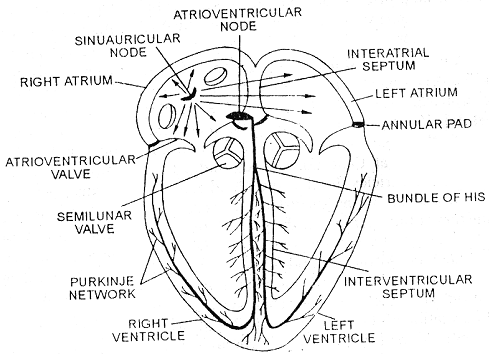
Started from S.A. node which stimulate A.V. node, A.V. node with the help of Bundle of His and purkenje fibres stimulate ventricles.
Heart beat is of 2 types -
(i) Neurogenic - Controled by nerve e.g. lower animals - Arthropoda, Mollusca. (ii) Myogenic - By own muscles. e.g. Vartebrates, Anopheles.
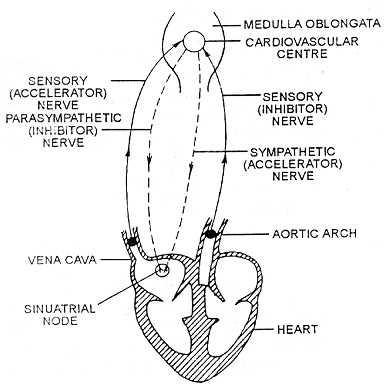
In rabbit and man it is myogenic. Neurogenic part is less. It is under control of upper part of medulla.
Sympathatic accelerate heart beat. Pera sympathatic or vagal inhibit heart beat. Adrenal, thyroxine increases heart beat.
Heart beat is - 210/ minute in rabbit. 72 / minute in man. 500 / minute in mice. 800 / minute in shrew. 25 / minute in elephant. 8 / minute in belenoptera.
In left ventricle pressure is 115-125 mm Hg. In right ventricle pressure is 25-30 mm Hg.
In man cardiac cycle is of 0.8 sec.
Heart beat is below normal is brachae cardia. Heart beat is above normal is tachae cardia.