LONG RUN OUTPUT
In the LR whether or not the firm makes profit will depend on the conditions of entry. For example, when surplus profits exist, there will be new entrants because they will make profit.
But as new firms enter, the market share enjoyed by each firm dwindles and their curves will shift to the Left. The costs will also be affected by the new entrants in three ways:
1. The new firms might make the cost resources to go up.
2. The cost curves might also be unaffected.
3. As new firms enter the cost curves might shift downwards because many sellers might force costs of resources downward.
But in the LR increasing costs are mostly likely. If there are increasing costs then existing profits will be squeezed. Because of the reduction in an individual firm's product, there will be a reduction in profits.
As long as there area profits in the industry, more firm's entry will stabilize when profits are ZERO. The losses might also cause exit of the firm's. The incentive to withdraw ceases when losses have been eliminated. Therefore the LR output and price of the firm looks like this:
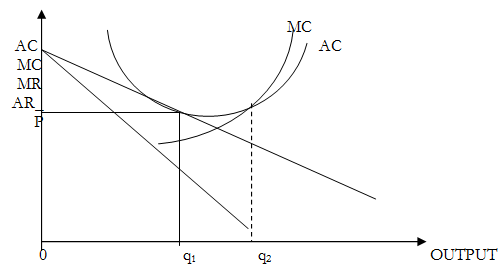
Zero profits imply that LRAC = LRAR. Therefore LRAC is tangent to AR at Q1. But Q2 is the LR optimum output for the firm but with a negatively sloped AR curve. Zero profits imply that each firm will utilize a scale of plant smaller than optimum. Hence free entry leads to EXCESS capacity for each plant.