Island Economy:
Consider an economy as a sea with islands of local markets. Each household produces goods and sells them on one and only one of the arrays of these markets. Goods differ according to location, physical characteristics, and so on. Accordingly, we index goods by the symbol z, where z = 1,2,...,n. The index might specify a location or be associated with an assemblage of characteristics of goods, methods of production etc. pt(z) is the price of a good or, indeed, a basket of commodities of type z during period t. Thus, the RELATIVE PRICE Pt(z)/pt(z') is the price of commodities of type or location z relative to commodities of type or location z′. Distinct is the GENERAL PRICE LEVEL pt which is the average of the prices in the islands at date t. If pt(z)> pt, then locale z appears relatively attractive to sellers in the given period. There will be a rush of productive resources from other employments to island z. The increased supply of goods in our market will, in the familiar manner, drive down the local price to the average price. Similar reasoning applies to a case when the price of the commodity/at the location z is less than the general price level. Assuming freedom of entry and exit, the average of all prices will be an efficient estimator of the local price. At the beginning of period t, a producer in market z has a stock of capital kt-1(z). Assuming a production function f with standard properties, the quantum of goods produced is given by yt(z) = f(kt-1(z),lt(z)). Total revenue earned by sellers from sales is the product of this quantity with the local price. However, people typically shop at different locations and the variable of interest to them will be pt, the index of generalized purchasing power. In that case, people will calculate the real value of the revenue from production which is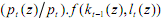 .
.
Thus, an increase in the relative price above, physical output remaining constant, means a greater value of sales. From the perspective of a producer, this increase is no different from a corresponding upward shift in the production function. Earlier, when deciding how much to work and produce, workers and producers looked at the physical marginal product of labour. Now, in order to calculate the effect on real sales revenue, producers multiply that number by the relative price to get the real value of the marginal product of labour. Then, as earlier, a shift in one component of the product, the relative price, appears identical to a proportional shift in labour's physical marginal product schedule. Consequently, producers respond in the familiar fashion.