Illustrates the quantum theory of black body radiation by Planck?
Planck’s quantum theory of black body radiation
Planck was investigating the properties of light-emitting and heat bodies. Typical physics had theories that predicted which the brightness of a body raises continuously as the frequency of its electromagnetic radiation is raised.
Regrettably, experiments revealed a completely different representation. The brightness did rise initially, but only up to a limit. After that, actually, this began to fall. We therefore get bell-shaped curves when we plot frequency against brightness.
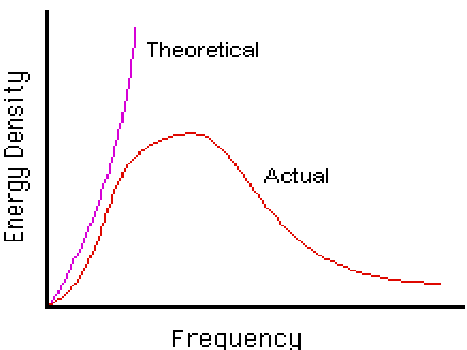
Intensity verses Frequency Plot
Besides, other observation was made: as bodies turn into hotter, their maximum brightness shifts in the direction of higher frequencies. It is why an object, heated from 300 to 400 C, emits mainly infra-red or heat waves. When the temperature is increased, the object seems to be red, in that case orange, and at last white or even blue. Classical theories completely failed to describe this discrepancy between the identified facts and the observations. After that, in the winter of 1900, Max Planck determined a solution to such problem. Planck ushered into the quantum period by making a bizarre assumption:
“Absorption and emission of energy can happen only into discrete amounts”
This might seem absolutely unsurprising to you, but believe, this shook the scientists of which period. Planck himself did not identify he would end up along with this statement! This was an entirely unexpected discovery, and yet that was only the beginning of what would come later. Planck termed these discrete lumps as quanta. That was against the entire world-view which had been built through the beginning. And therefore the quantum revolution began.