How numbering plan is achieved in modern telephony? Give the structure with example.
The objective of numbering plan is to uniquely identify every subscriber connected to a telecommunication network. A numbering plan may be semi-open or open or may be closed. An open-numbering plan permits broad variation in the number of digits to be used to specify a subscriber in a multi exchange area or within a country. This plan is utilized in countries equipped extensively with non-Director Strowger switching systems. In these cases the numbering scheme is generally an exact image of the network structure changes. A semi-open plan permits number lengths to be different by almost one or two digits. Now, this scheme is the most common and is utilized in many countries involving India. In the Uniform numbering scheme or closed numbering plan, the number of digits in a subscriber number is not changed. An international numbering plan or world numbering plan has been explained by CCITT in recommendations of this E.160-E.163. For numbering reasons, the world is divided in zones as demonstrated in figure. Each zone is specified a single digit code. For the European zone two codes have been allotted due to the large number of countries in this zone. All international telephone number contains two parts as demonstrated in figure. The country code consists of one, two or three digits, the first digit being the zone code wherein the country lies. If an integrated numbering plan already covers a whole zone, the countries in which zone are identified through the single digit zone code itself.
The existence of world numbering plan places limit on the national numbering plan of all countries. The number of digits in an international subscriber number is restricted to an absolute maximum of 12. In practical, with a few exceptions, world numbers are limited to 11 digits. Accordingly, the number of digits available for a national numbering plan is 11-N, here N is the number of digits in the country code.
Generally, a national number consist of three parts as demonstrated in figure. The area or the trunk code specifies a particular numbering area or the multi exchange area of the called subscriber, therefore determine the routing for a trunk call and a charge for this. As per to CCITT international usage, a numbering area is identified such as area wherein any two subscriber use equal dialing procedure to reach any other subscriber into the network. An exchange code specifies a particular exchange in a numbering area. This determine the routing for incoming trunk call from other numbering area or for a call originating from one exchange and destined to other in similar numbering area. Subscriber line number is utilized to select the called subscriber line on the terminating exchange. In a CCITT terminology, the combination of the exchange code and the subscriber line number is termed as the subscriber number that is the number listed in the telephone directory.
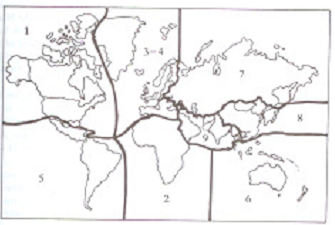
FIG - World Numbering Zones
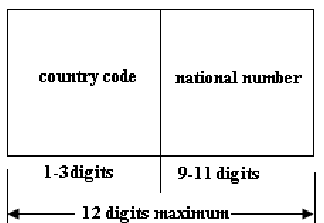
FIG - International Telephone Number

FIG - National Telephone Number