History of Information Technology and Organisations
The increasing sophistication in information systems and the growth in their use have been influenced by three main factors:
- Increasing and relentless pressures on organisations to perform.
- The rate of change in enabling technology.
- The increasing complexity of products and services that require increasing amounts of information to support their production and delivery.
The diagram overleaf illustrates how IS has invaded the operations of the business across the last 40 years.
Stage 1 signifies a simple system that has been implemented discretely to aid the operation of one particular function - this may be a stock control system that is used within a store or a simple spreadsheet system used in the finance department. This type of system typically began to appear during the late 1960s and early 1970s.
Stage 2 shows the proliferation of these discrete systems throughout the organisation and characterises the trends during the late 1970's and early 1980's, therefore the stock control system maybe accompanied by a cost control system within the finance department and a configuration control system within the engineering department. The key point is that each system will still be operating in isolation from the others and, due to crude Human Machine Interface (HMI) these systems may have been difficult to use requiring special skills and training.
Stage 3 illustrates the changes since the 1980's with the linking of these discrete systems to become an integrated whole where the stock control system, the finance system and the configuration control system maybe integrated with a procurement system to make an Material Resource Planning (MRP) system using a common database and communication interfaces. This stage usually signifies the point at which the organisation becomes dependant on the IS as most of the important information and many of the critical functions are now carried out 'to the beat of the system'. It is also important to note that from a historical point of view often the IS was overlaid upon the previous manual systems in piecemeal way. This means that this period was often characterised by integrated, but sub-optimal and difficult to operate systems.
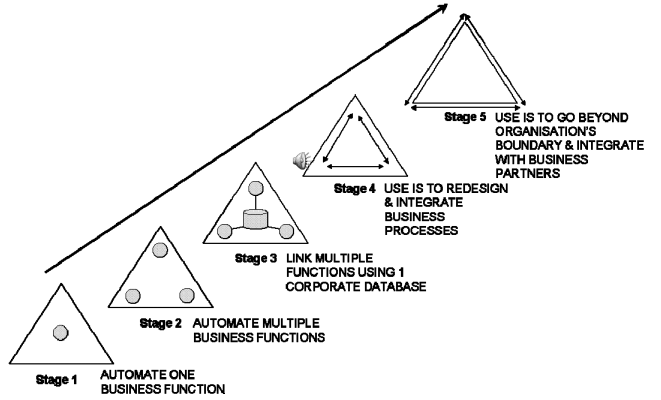
Stage 4 however signifies that more recently as technology has become more sophisticated both in processing power and more importantly in Human Machine Interface (HMI) it has been possible to re-engineer business processes to be built around the information system in the first instance leading to a more streamlined process rather than a manual process with the IS working as a bolt-on. The nature of the HMI and the rise in 'windows' based systems also allows easier use so making for a business that truly works with the system. This is illustrated by the rise in Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems that control all aspects of the business including provision of human resources, and planning of future business.
Stage 5 indicates that the rise in communications technology enablers now allows business systems to span whole markets and link businesses up and down supply chains. An example could by the electronic transfer of design data using common file formats to enable joint product development programs between partner companies.
More recently the Internet has become a major force in inter-company collaboration and communication. While this diagram indicates an evolution across time beginning at Stage 1 with systems that are limited in scope, simple in operation and stand-alone, to Stage 5 with systems that encompass entire organisations or markets, are complex in operation and fully integrated, it is important to note that all organisations must decide, depending upon their particular business needs and resources, what type of IS they should implement. Although this diagram shows a progression with Stage 5 as the pinnacle, a system of this sophistication may not be the most useful or practical for every organisation even in the 21st century.