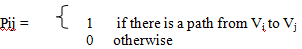Q. Define the graph, adjacency matrix, adjacency list, hash function, adjacency matrix, sparse matrix, reachability matrix.
Ans.
Graph is explained below
A graph G, comprises of 2 sets V & E. V is a finite non-empty set of vertices. E is a set of pairs of vertices, these pairs are known as edges.
Adjacent Matrix can be defined as follows:-
Let G=(V,E) be graph with n vertices, n>=1.
In The Adjacency Matrix of G is a 2- dimensional which are n*n array , say A, with the property that A(i,j) = 1 iff the edge (vi,vj) ( < vi, vj> for the directed graph) is in E(G). A(i,j)= 0 if there is no edge in G.
Adjacency Lists can be defined as follows
In this type of representation the n rows of the adjacency matrix are represented as n linked list. There is only one list for each vertex in G. The nodes in list signifies the vertices that are neighbouring from vertex i.
Hash Function is described below
A hash function h is simply a mathematical formula which manipulates the key in
some form to compute or calculate the index for this key in the hash table Commonly, we say that a hash function h maps the universe U of keys into the slots of a hash table T[0....n-1]. This process of mapping keys to appropriate slots in a hash table is called hashing.
Sparse Matrix is described below
A m x n matrix A is called to be sparse if and only if most of its elements are zero. A matrix which is not sparse is known as the dense matrix. for example:
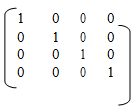
Reachability Matrix /Path Matrix is described below:-
Let G be a easy directed graph with m nodes, V1, V2, V3........Vm. The reachability matrix of G is the m -square matrix P=(Pij) explained below