Fraction Defective P Chart - Control Charts for Attributes
This type of chart is used when it is impractical or inconvenient to maintain a constant sample size. Instead of plotting the number of defectives in each sample, the proportion (p) or fraction of defectives is calculated and then plotted. Clearly, to ensure that meaningful plots are made, the sample sizes must be large enough to ensure that a number of defectives will typically be found. This may seem to imply that some level of non-conformance is being accepted, but this is not necessarily so. For example, consider the Go/Not-go gauging example shown in the figure on page 249. Whilst the design limits of size on the component diameter might be, say, 24.98 mm and 25.02 mm; for process control purposes the gaps in the gauge might be set at, say, 24.99 and 25.01 respectively. Remembering that, for attributes, only two states are possible (defective/non defective) the relevant probability distribution is the binomial distribution, the mean of which (¯p) can be estimated by inspecting a large number of items:
¯p = total number of defectives/ total number inspected
An estimate of the standard deviation of the binomial distribution (σp), for samples of size n is given by:
σp = √(¯p (1-¯p) / n)
For small values of n the profiles of the binomial distributions are distinctly skewed, but, for large values of n and, particularly, when the product p n is greater than about 5, the distributions are sufficiently symmetrical to be well-approximated by the normal distribution. In this latter situation the control chart limits can be determined in the same manner as for variables charts.
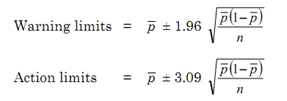
It will be realised that the implied constant sample size (n) in these expressions presents some difficulty in a procedure when the sample size is allowed to vary. This can be surmounted by using an average value for n, and limiting variation in the size of subsequent samples to, say, ±20 per cent of this value: the results will still be sufficiently accurate for most process control purposes.