Q. Explain working of three-phase transformers?
Transformation in three-phase systems can be accomplished in either of two ways: (1) connecting three identical single-phase transformers to form a three-phase bank (each one will carry one-third of the total three-phase load under balanced conditions); or (2) a three-phase transformer manufactured for a given rating. A three-phase transformer, compared to a bank of three single-phase transformers, for a given rating will weigh less, cost less, require less floor space, and have somewhat higher efficiency.
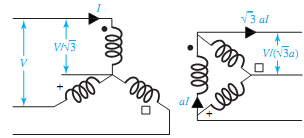
The windings of either core-type or shell-type three-phase transformers may be connected in either wye or delta. Four possible combinations of connections for the three-phase, two- winding transformers are Y-�Δ, Δ�-Y, Δ�-Δ�, and Y-Y. These are shown in Figure with the transformers assumed to be ideal. The windings on the left are the primaries, those on the right are the secondaries, and a primary winding of the transformer is linked magnetically with the secondary winding drawn parallel to it. With the per-phase primary-to-secondary turns ratio (N1/N2 = a), the resultant voltages and currents for balanced applied line-to-line voltages V and line currents I are marked in the figure.
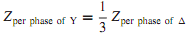
As in the case of three-phase circuits under balanced conditions, only one phase needs to be considered for circuit computations, because the conditions in the other two phases are the same except for the phase displacements associated with a three-phase system. It is usually convenient to carry out the analysis on a per-phase-of-Y (i.e., line-to-neutral) basis, and in such a case the transformer series impedance can then be added in series with the transmission-line series impedance. In dealing with Y-�Δ and Δ�-Y connections, all quantities can be referred to the Y-connected side. For �Δ-�Δ connections, it is convenient to replace the �-connected series impedances of the transformers with equivalent Y-connected impedances by using the relation.
It can be shown that to transfer the ohmic value of impedance from the voltage level on one side of a three-phase transformer to the voltage level on the other side, the multiplying factor is the square of the ratio of line-to-line voltages, regardless of whether the transformer connection is Y-Y, Δ�-Y, or Δ�-Δ�. In some cases, where Y-Y transformation is utilized in particular, it is quite common to incorporate a third winding, known as tertiary winding, connected in delta. Such multiwinding transformers with three or more windings are not considered in this text.