Explain the working of Transformers
A transformer often uses a core, which looks like a square donut of iron, to change the voltage applied to the primary coil to a new larger or smaller voltage on the secondary coil.
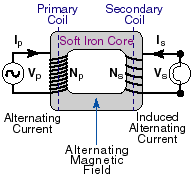
The current caused by the voltage in the primary coil generates a magnetic field, which extends to all parts of the iron. This extended magnetic field then causes a voltage in the secondary coil, but if the primary coil has fewer loops than the secondary, the voltage out will be larger than the applied voltage.

Where Vs is the voltage in the secondary coil in volts and Vp is the voltage in the primary coil in volts. If both primary and secondary coils have an equal number of loops, the voltages will be the same on both sides. If the secondary coil has more loops than the primary, the voltage out will be more than the applied voltage, and the transformer is a step-up transformer. If the primary coil has more turns than the secondary, the voltage out will be less than the applied voltage, and the transformer is a step-down transformer.
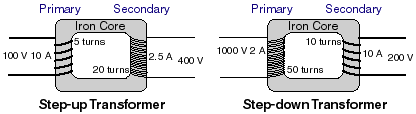
Since the energy (and therefore the power) in has to equal the energy (or power) out, conservation of energy still holds, and the power in the primary Pp = Ip Vp must equal Ps = Is Vs. While the voltage increases,
Ip Vp = Is Vs
so that the current in the secondary, Is, must decrease to have the same product. If this is an ideal transformer, so that it loses no energy, the previous equation will help calculate Is if Vs is known. However, if the transformer is real and has less than 100% efficiency,

where Power is in watts, and efficiency is a fraction less than one or a percent out of 100%. The rest of the energy is turned to heat through the resistance of the wire, magnetization and demagnetization of the core, and eddy currents in the core.
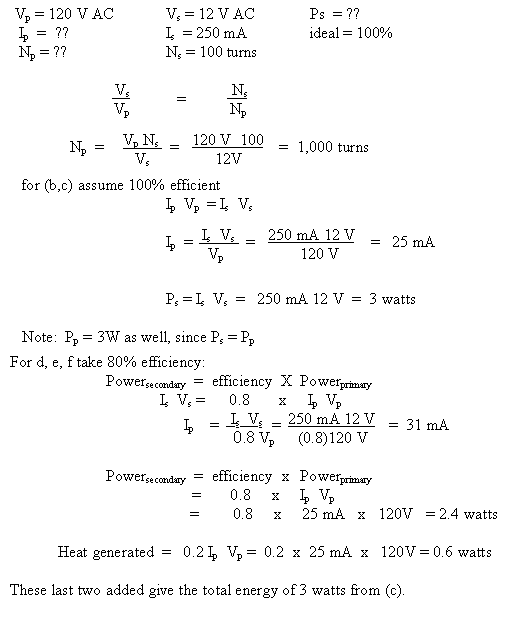
Example- A step-down transformer is used to change 120 V AC from the wall plug to 12V AC. If the secondary coil has 100 turns and supplies 250 mA of current...
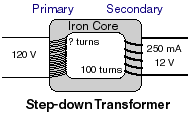
- How many turns are in the primary coil?
- What is the current in the primary coil (assuming the transformer is 100% efficient)?
- How much power is transformed if the transformer is ideal?
- How much power if the transformer is only 80% efficient?
- What is the current in the primary coil if it is 80% efficient?
How much heat would it generate at 80% efficiency?
All of the examples in this section - cathode ray tubes, oscilloscopes, monitors, televisions, motors, generators and transformers - depend on the relationships among magnetic fields, electric currents and wires, and electromagnets.