With the help of a truth table explain the working of a half subtractor. Draw the logic diagram using gates.
Ans:
Half Subtractor: For the subtraction of B (subtrahend) from A (minuend) in a logic circuit, where A and B are 1-bit numbers is termed to as a Half-Subtractor. The truth table of half subtractor is illustrated in below. Now there A and B are the two inputs and Di that is difference and Bo that is borrow are the two outputs. If B is larger than A (for example, A=0 and B=1), a borrow is essential,
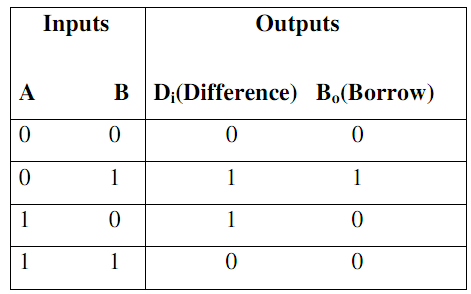
Truth Table no.1
By the Truth Table, the logical expressions for Di and Bo are acquired as
Di = A‾ B + A B‾
BO = A‾ B
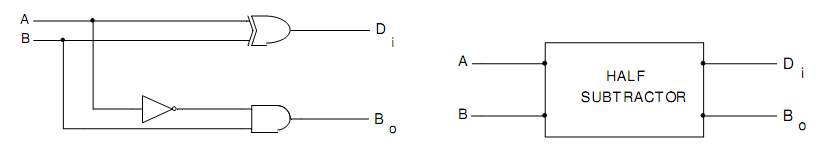
Fig.(a) Logic Diagram of Half Subtractor Fig.(b) Block Diagram of Half Subtractor
In Table, input variable B is subtracted from A to provide output Di difference. If B is larger than A (for example, A = 0 and B = 1), borrow is essential. In the Truth Table, inputs are A and B, Outputs are Di (difference) and B0 (borrow). Therefore, the Boolean expressions for the half subtractor by the Truth Table can be written as
Di = A ⊕ B ---------(1)
BO = A‾ B --------(2)
Through combining Boolean Expressions (1) and (2), we find the logic circuit for Half Subtractor demonstrated in fig.(a) and its block diagram is demonstrated in fig.(b).