Explain the several terms ATP, NAD, and FAD ?
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) is an ester, an organic compound formed from a reaction between carboxylic acid and an alcohol. ATP is composed of adenosine, adenine bonded to ribose (a 5-carbon sugar), and three phosphate groups linearly bonded to another carbon on the ribose.
ATP is unusual in that the bonds of the terminal phosphate groups release an extraordinarily high amount of free energy when broken in hydrolysis. The change in free energy (DG) that results from breaking the first bond is about 10-12 kcal/mole, more than twice the energy given off when a typical phosphate bond is broken. Thus, the bonds of the second and third phosphate groups of ATP are high-energy bonds, represented by a tilde (~) in chemical formulas. The structure of ATP is written as A-P~P~P, with the A standing for adenosine, and the second and third phosphate bonds represented as high-energy.
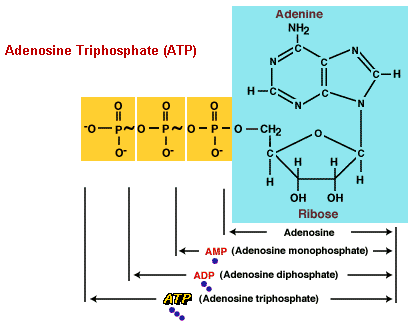
ATP undergoes hydrolysis, catalyzed by the enzyme ATPase, when its energy is required for a metabolic process. The first high-energy bond is broken, releasing a phophate ion and energy, and converting ATP into a 2-phosphate molecule, adenosine diphosphate (ADP). The liberated phosphate ion, HPO42-, is generally abbreviated P; meaning inorganic phosphate. The second high-energy bond may also be broken, releasing another phospate and additional energy, and converting ADP into a 1-phosphate molecule, adenosine monophosphate (AMP).
ATP is re-phosphorylated (has its phosphate groups reattached) by input of energy from another exergonic reaction in the presence of another enzyme, ATP synthetase. Actually, many different enzymes catalyze the formation and breakdown of ATP in cells.
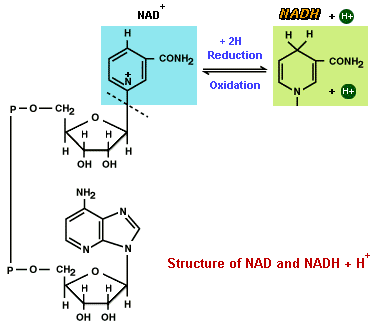
NAD and FAD are compounds that enter into oxidation-reduction reactions with very high values of DG (free energy). NAD can exist in either the oxidized form of NAD, or in the reduced form of NADH + H+. Oxidation of NADH + H+ in the presence of oxygen gas yields a DG of -52.4 kcal. The sign of DG is negative, meaning the reaction is exergonic. NAD and FAD are formed from the vitamins niacin andriboflavin. Since these molecules are recycled, the vitamin B complex required from food is low.