Explain the Prisms, Dispersion and Color
A ray of white light that passes through a prism is dispersed into the visible spectrum. Red light is refracted the least, and purple light is refracted the most. This is because the speed of the various wavelengths in glass is different, slowest for violet light and fastest for red light.
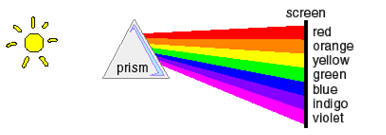
Originally, prisms were used in machines called monochromators to spread the spectrum of light coming from the stars. Now we can lose less light by using high resolution diffraction gratings to disperse the light into a rainbow. The first indication of which elements were present in stars was deduced from the spectrums obtained this way: these spectrums were observed to have dark bands in them. The dark bands were matched to absorption at the same wavelengths by elements on earth, and we were able to tell what elements were present in a given star. As the wavelength of these absorption bands shifted, we were able to measure Doppler shifts and the speed of the stars towards or away from Earth.
Color by Subtraction
Why do green leaves appear green? Why does any colored object appear to be the color it is to our eyes? The answer is that a pure green object appears green because green is the major color that is reflected to our eyes. Most of the other colors that make up white light are absorbed by the object.
Recall that sunlight is composed of all of the colors of the rainbow, and these colors correspond to different wavelengths of radiation. So if all of the wavelengths were absorbed, no light would be reflected to our eyes, and the object would appear to be black. If all of the colors were reflected, and none absorbed, the object would appear to be white! So if an object is orange, mostly orange wavelengths and some of the adjacent wavelengths of red and yellow are also reflected to our eyes, and we perceive the color of orange. If you were to shine a red light on a green object in a totally dark room, there would be no green light to be reflected to your eyes, and the color of the green object would appear black!
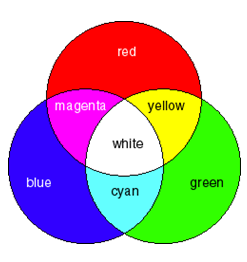
Color mixing for light is a little different than what you learned in art class with paint or pigments. Light is considered to have the primary colors of red, green, and blue. This is where the term "RGB monitor" comes from. Any color can be made as a different combination of the primary colors. Light’s secondary colors are magenta, yellow, and cyan. If you mix red and green, you get yellow light, the complement of blue, as shown on the chart. White light can be obtained by mixing complementary colors, such as blue and yellow.