Explain the life cycle of a process
Each procedure has a life cycle, which consists of execution, creation and termination phases of the procedure. A method may create several new procedures, which in turn may also generate still new processes, using system calls. In UNIX operating system environment, a new procedure is produced by fork system call. Process creation needs the following four actions:
i) Setting up the process description: Setting up the process description needs the creation of a Process Control Block (PCB). A Process Control Block contains basic data such as owner, process identification number, process status, explanation of the allocated address space and other completion dependent process specific information needed for procedure management.
ii) Allocating an address space: There are only two ways to allocate address space to processes; allocating separate space to each process or distribution the address space among the created processes.
iii) loading the program into the allocated address space: The executable program file is overloaded into the allocated memory space.
iv) Passing the process description to the process scheduler: The process created is then conceded to the process scheduler who distributes the processor to the competing processes.
The process implementation phase is controlled by the process scheduler. Process scheduling may be per process or per thread. The process scheduling involves three concepts: process states, state transition diagram and scheduling policy.
A process may be in one of the following states given below:
- New: The process is being formed.
- Running: The process is being implemented on a single or multiple processors.
- Waiting: The process is to come for some event to occur.
- Ready: The process is prepared to be implemented if a processor is available.
- Terminated: The process has completed execution.
At any time a procedure may be in any single of the above said states. As soon as the process is announce into the job line, it goes into equipped state. When the process scheduler transmits the process, its state turn into running. When the process is completely implemented then it is completed and we say that it is in the completed state. However, the process may return to ready state due to some type of interruption or may go to in waiting state because of some I/O activity. When I/O activity is finished it may go to ready state. The state transition diagram shown in figure 3:
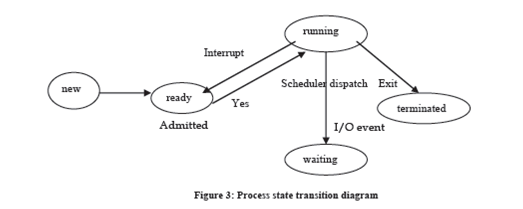
The scheduling policy may be both non pre-emptive and pre-emptive. In pre-emptive policy, the process may be distructed. OS had dissimilar scheduling policies. One of the common policies is First In First Out (FIFO) to select the process to be implemented. When the process finished implementation it is terminated by system calls like abort.