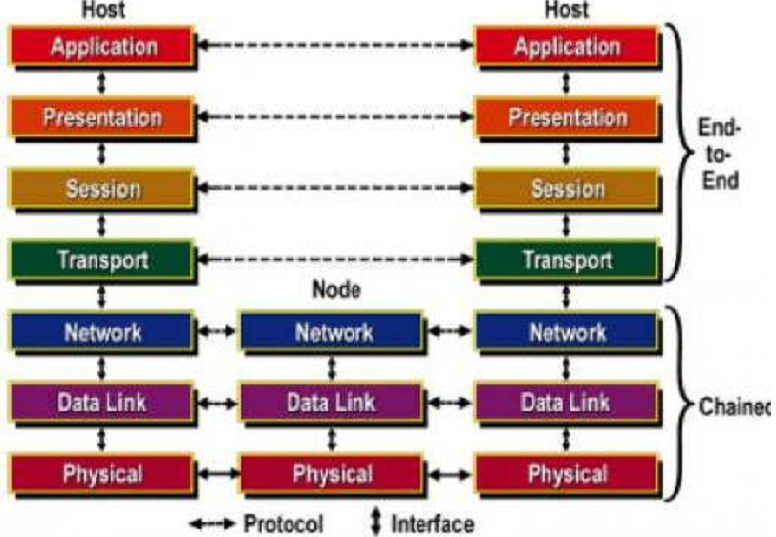
The OSI Reference Model:
The OSI model is based on a proposal developed by the International Standards Organization (ISO) as a first step toward international standardization of the protocols used in a variety of layers (Day and Zimmermann, 1983). It was changed in 1995(Day, 1995). The model is known the ISO-OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) Reference Model since it deals with linking open systems which is systems that are open for statement with other systems. The OSI model contains seven layers.
The principles that applied to arrive at the seven layers can be briefly summarized as follows:
1. A layer has to create where a different abstraction is required.
2. Each layer must perform a well-defined function.
3. The function of each layer must be chosen with an eye toward defining internationally consistent protocols.
4. The layer boundaries will be chosen to minimize the information flow across the interfaces.
5. The number of layers has to large enough that distinct functions need not be thrown together in the same layer out of necessity and small enough that the architecture does not become unwieldy.
The Physical Layer:
The physical layer is concerned with transmitting raw bits greater than a communication channel. The design subject has to do with making certain that when one side sends one bit, it is inward by the other side as one bit, not as a 0 bit.
The Data Link Layer:
The major task of the data link layer is to transform a raw transmission facility into a line which appears free of undetected transmission errors to network layer. It completes this task having dispatcher break up the input data into data frames (typically a few hundred or a few thousand bytes) and transmits frames successively. If the service is reliable, the receiver confirms correct receipt of each frame by sending back an acknowledgement frame. Another question that arises in the data link layer (and most of the higher layers as well) is how to keep a fast transmitter from drowning a measured receiver in data. Little traffic regulation mechanism is frequently needed to let the transmitter know how much buffer space the recipient has at the moment. Often, these flow regulations as well as the error handling are integrated.
The Network Layer:
The network layer pedals the operation of the subnet. The key design issue is determining how packets are routed from source to destination. Routes could be on the basis of static tables that are ''''wired into'''' the network and hardly ever changed. They can be strong-minded at the start of each conversation such as a terminal session. Ultimately they can be highly dynamic, being determined new for each packet, to reflect the existing network load. If a large number of packets are present in the subnet at the same time and they will get in one another way, forming bottlenecks. The control of such blocking also belongs to the network layer. More generally, the value of service provided (delay, transit time, jitter, etc.) is also a network layer issue. If a packet has to travel from one network to another to get to its destination, many problems could arise. The addressing used by the second network might be different from the first one. The second one may not accept the packet at all as it is too large. The protocols can differ. It is up to the network layer to conquer all these problems to let heterogeneous networks to be interconnected. In broadcast networks, the routing difficulty is easy, so the network layer is frequently thin or even nonexistent.