Explain Composition of Human Milk?
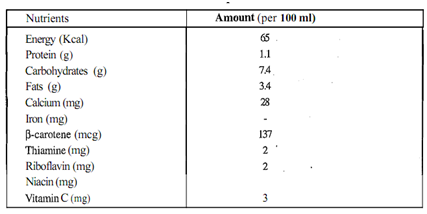
Research clearly shows that each type of mammalian milk is unique and consists of a highly complex mixture of organic and inorganic compounds. Human milk is a solution of proteins, sugar and inorganic compounds in which a variety of fatty acids are suspended. Its nutritional composition is presented in Table,
Milk composition varies between mothers (inter-individual variation) from one period of lactation to the next (intra-individual aviation) and even within a single 24-hour period (diurnal variation) and the time during the feed, as well as, the breast. The composition of milk is also related to the amount secreted, timing of withdrawal and individual variations, which includes maternal age, parity, health and socio-economic status. Gestational age of the infant also affects, since milk from mothers of premature infants has higher concentrations of some nutrients as compared to milk from mothers of term infants. Similarly, diet and use of oral contraceptives may also influence composition.
The concentrations of most nutrients fall between certain limits in the milk of healthy well-nourished mothers. The caloric value of human milk depends mainly on the fat content. Even after prolonged lactation for 2 years or more, the quality of milk produced by Indian and African women appears to be relatively well-maintained, although the quantity may be small.
• Special characteristics of colostrum, beneficial to the infant are summarized here in:
• Volume of of colostrum 2-10 ml/feeding/day - related in part to the parity of the mother
• Typically yellow, due to a relatively high carotene content
• Transparent, contains more protein, less sugar and much less fat
• Lower in calories than mature milk (58 vs. 70 Kcal/OO ml)
• Concentration of sodium, potassium, and chloride greater than in mature milk
• Facilitates establishment of 'bifidobacteria' in the gastrointestinal tract of newborn
• Facilitates passage of meconium in the newborn's intestines
• Abundant content of antibodies - passive immunity for infant.
Colostrum changes to transitional milk between the 3rd and 6th day at which time the protein content is still quite high . By the both day, major changes have been completed. By the end of the 1st month, the protein content reaches a consistent level. As the content of protein falls, the content of lactose and fat progressively rise, as lactation becomes more firmly established.