Example of Indirect Taxes and Subsidies- ACCOUNTING SYSTEM
We now permit our government to impose what are called indirect taxes. This category includes sales tax, excise tax, customs duties, etc. These taxes are treated as cost of doing business by the producing enterprises but there is no corresponding factor payment or purchase. Conceptually, we can say that the enterprises are purchasing productive services from the government and paying for them by means of these taxes. These can then be treated as intermediate inputs. However, as we saw, it is impossible to identify a particular component of taxes as a payment for a particular component of government services. Government services, financed from a general tax pool, contribute to both production and consumption. Hence in national accounts the convention is to treat indirect taxes as part of the producer's price and hence are included in the market value of final outputs.
Now value added or factor payments will not add up to GNP defined as market value of final outputs inclusive of indirect taxes. Look at the following accounts which are a modified version of those in example VI.
Production Sector
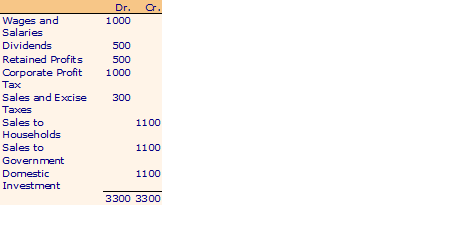
Government

Household Sector

saving and Investment Account

Now GNP at market prices = C + I + G
= 1100 + 1100 + 1800 = 4000
Total value added = GNI = GNP at factor cost
= 1700 (Wages and Salaries) + 2000 (Gross Profits) = 3700
Now GNP at market prices does not equal GNI. The latter is also called GNP at factor cost. We have
GNP at market prices - Indirect taxes = GNP at factor cost
How come with incomes of 3700, the society is able to consume output worth 4000? The answer lies in the fact that government services worth 300 are also consumed for which no explicit payment is made. They are paid for through indirect taxes imposed on marketed output.
This way of treating indirect taxes assumes that these taxes are fully passed on to the consumer. If government is subsidizing certain productive activities subsidies are to be treated as negative indirect taxes, i.e. as a 'factor payment' which does not add to the price of the product. Thus,
GNP at Factor Cost = GNP at Market Prices - Indirect Taxes + Subsidies
We now define the following income and product concepts:
GNP at Factor Cost = GNP at Market Prices - Indirect Taxes + Subsidies
NNP at Factor Cost (National Income) = GNP at Factor Cost - Depreciation
Personal Income = NNP at Factor Cost - Corporate = Profit Taxes - Retained Profits
Personal Disposable Income = Personal Income - Personal Income Tax
As mentioned in the text, government expenditure G includes only expenditure on current goods and services. It does not include transfer payments.