Deadlock And Its Prevention: As seen earlier, though two phase locking protocol handles the trouble of serialisability, but it causes some troubles also. For instance, consider the given two transactions and a schedule involving these transactions:
TA TB
X_lock A X_lock A
X_lock B X_lock B
: :
: :
Unlock A Unlock A
Unlock B Unlock B
Schedule
T1: X_lock A
T2: X_lock B
T1: X_lock B
T2: X_lock A
As is clearly seen, the schedule causes a trouble. After T1 has locked A, T2 locks B and then T1 tries to lock B, but not able to do so waits for T2 to unlock B. Likewise T2 tries to lock A but search that it is held by T1 which has not yet unlocked it and therefore waits for T1 to unlock A. At this stage, neither T1 nor T2 can go on since both of these transactions are waiting for the other to unlock the locked resource.
Clearly the schedule come to a halt in its implementation. The main thing to be seen here is that both T1 and T2 follow the two phase locking, which guarantees serialisability. So when the above type of case arises, we say that a deadlock has occurred, hence two transactions are waiting for a condition that will never happen.
Also, the deadlock can be defined in terms of a directed graph known as a "wait for" graph, which is maintained by the lock manager of the DBMS. This graph G is described by the pair (V, E). It haves of a set of vertices/nodes V is and a set of edges/arcs E. Every transaction is represented by node and an arc from Ti →Tj, if Tj holds a lock and Ti is waiting for it. When transaction Ti needs a data item presently being held by transaction Tj then the edge Ti → Tj is inserted in the "wait for" graph. This edge is deleted only when transaction Tjj is no longer holding the data item required by transaction Ti.
A deadlock in the system of transactions happens, if and only if the wait-for graph having a cycle. Every transaction involved in the cycle is said to be deadlocked. To notice deadlocks, a periodic check for cycles in graph can be completed. For instance, the "wait-for" for the schedule of transactions TA and TB as above can be made as:
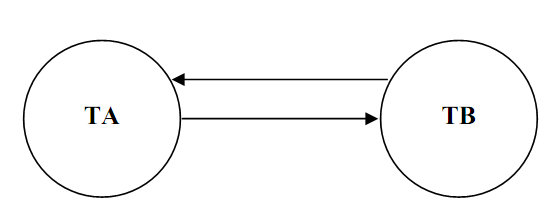
Figure: Wait For graph of TA and TB
In the above figure, TA and TB are the two transactions. The two edges are present among nodes TA and TB since each one is waiting for the other to unlock a resource held by the other, forming a cycle, causing a deadlock trouble. The above case shows a direct cycle. Though, in real situation more than two nodes may be there in a cycle.
A deadlock is therefore a situation that can be formed because of locks. It causes transactions to wait forever and thus the name deadlock. A deadlock happens because of the following conditions:
a) Mutual exclusion: A resource can be locked in exclusive mode by only single transaction at a time.
b) Non-preemptive locking: A data item can only be unlocked by the transaction that locked it. No other one transaction can unlock it.
c) Partial allocation: A transaction can obtain locks on database in a piecemeal fashion.
d) Circular waiting: Transactions lock part of data resources required and then wait indefinitely to lock the resource presently locked by other transactions.
In order to avoid a deadlock, one has to ensure that at least one of these conditions does not happen.
A deadlock can be avoided, prevented or controlled. Let us talk about a simple method for deadlock prevention.