Datatype Conversion
At times it is necessary to convert a value from one datatype to another. For e.g. if you want to inspect a rowid, you should convert it to a character string. The PL/SQL supports both the explicit and implicit (automatic) datatype conversion.
Explicit Conversion
To convert the values from one datatype to other, you use the built-in functions. For e.g. to convert a CHAR value to a DATE or NUMBER value, use the function TO_DATE or TO_NUMBER, respectively. On the contrary, to convert a DATE or NUMBER value to the CHAR value, you use the function TO_CHAR.
Implicit Conversion
When it makes sense, the PL/SQL can convert the datatype of a value implicitly. This permits you to use the variables, literals, and parameters of one type where the other type is expected. In the example shown below, the CHAR variables start_time and finish_ time hold string values representing the number of seconds in the past midnight. The variation between those values must be assigned to the NUMBER variable elapsed_time. And hence, the PL/SQL converts the CHAR values to the NUMBER values automatically.
DECLARE
start_time CHAR(5);
finish_time CHAR(5);
elapsed_time NUMBER(5);
BEGIN
/* Get system time as seconds past midnight. */
SELECT TO_CHAR(SYSDATE,'SSSSS') INTO start_time FROM sys.dual;
-- do something
/* Get system time again. */
SELECT TO_CHAR(SYSDATE,'SSSSS') INTO finish_time FROM sys.dual;
/* Compute elapsed time in seconds. */
elapsed_time := finish_time - start_time;
INSERT INTO results VALUES (elapsed_time, ...);
END;
Before assigning a selected column value to a variable, the PL/SQL will, if necessary then convert the value from the datatype of the source column to the datatype of the variable. This happens, for e.g. If you select a DATE column value into a VARCHAR2 variable.
Similarly, before assigning the value of a variable to a database column, the PL/SQL will, if necessary then convert the value from the datatype of the variable to the datatype of the target column. If the PL/SQL cannot determine that implicit conversion is required, you get a compilation error. In such situation, you should use a datatype conversion function. The table shows that implicit conversions PL/SQL can do.
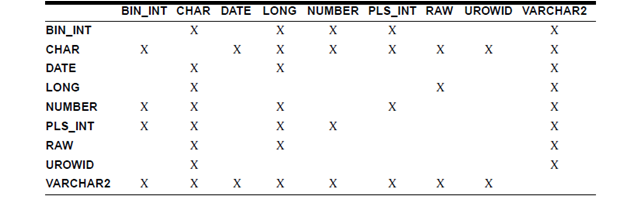
It is your duty to ensure that the values are convertible. For illustration, the PL/SQL can convert the CHAR value '02-JUN-92' to a DATE value but cannot convert the CHAR value 'YESTERDAY' to a DATE value. Likewise, the PL/SQL cannot convert a VARCHAR2 value containing the alphabetic characters to a NUMBER value.
Implicit versus Explicit Conversion
Normally, to rely on the implicit datatype conversions is a poor programming practice as they can hamper the performance and might change from one software release to the next. Also, the implicit conversions are context sensitive and hence not always predictable. Rather, use datatype conversion functions. In that way, your applications will be easier and reliable to maintain.