Explain with the help of Nyquist theorem, the data rate limitations in PSTN's.
Data rates in PSTNs: A voice channel in a public switched telephone network is band restricted with a nominal bandwidth of 3.1 kHz. A first-cut estimate of it can be acquired from Nyquist's theorem that applies to noiseless states and channels:
R = 2H log V bps
Where
R = maximum data rate
H = bandwidth of the channel
V = number of discrete levels in the signal
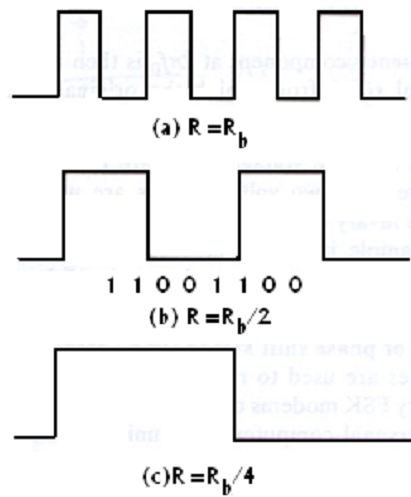
FIG - Baud Rates and Bit Rates
For a 3-kHz channel and a binary signal, the maximum data rate works out to be 600 bits per second, when the channel is ideal. In the practical channel, the maximum rate would come down. Through increasing the number of levels used to signify the signal, the bit rate may be raised arbitrarily in a noiseless channel. This is significant to recognize that the actual number of signal transitions is even limited to the binary level limit; the effectual bit rate goes up with more than two signal levels when each signal level can represent a group of two or more bits. Now, the maximum rate of signal transitions which can be supported by a channel is termed as baud rate or symbol rate. In a channel, there is an absolute maximum limit for the bit rate where noise is present. This limit occurs since the difference MONG two signal levels becomes comparable to the noise level while the number of signal level is raised.
Claude Shannon, who was extend Nyquist's works to the case of noisy channels influenced by thermal or random noise. Result states of Shannon:
R = H log (1+S/N)
Here R= the maximum bit rate obtainable
H= bandwidth of the channel
S/N = signal to noise ratio.