Cost-volume relationship:
Cost-volume relationship is illustrated through a simple example dealing with the cost of operating an automobile. To perform the analysis following cost regarding owning and operating an automobile is supposed.
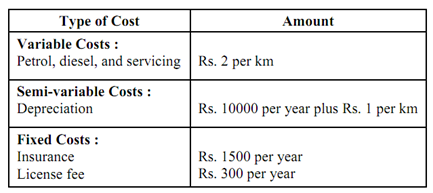
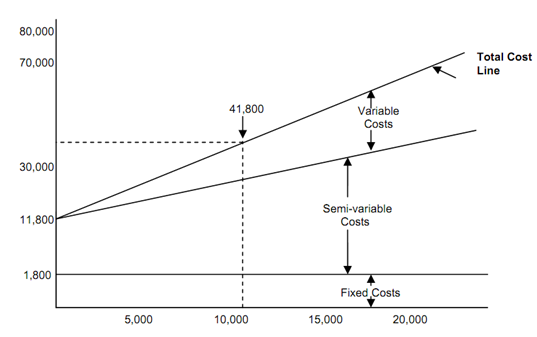
Figure: Cost Volume Relationship
The cost-volume-relationship may be expressed graphically. The relation among volume (miles per year) and different type of costs (that means. fixed, variable and semi variable) is illustrated in Figure
The estimated automobile cost per annum for any assumed mileage may be determined from the graph of total cost. For instance, to drive 10,000 km in a given year a total cost of Rs. 41800 or Rs. 4.18 per km is estimated. By combining all of the fixed and variable elements of the cost, the cost of owning an automobile can be estimated as Rs.11800 per year plus Rs. 3 per km driven during the year.
The effect of volume on unit (per km) costs may be calculated through the conversion of net costs into average costs as described below:
Cost per Mile of Owning and Using an Automobile
Miles driven 5,000 10,000 15,000 20,000
Costs:
Completely variable (Rs. 2Per km) 10,000 20,000 30,000 40,000
Semi variable:
Variable part (Rs.1 per km) 5,000 10,000 15,000 20,000
Fixed part 10,000 10,000 10,000 10,000
Fixed Costs (1500 + 300) 1,800 1,800 1,800 1,800
Total Costs 25,800 41,800 56,800 71,800
Cost per km 5.16 4.18 3.78 3.59
From the aforementioned analysis it may be seen that the variable portion of the costs raise with the increase in volume but the rate of change in variable cost remains constant. On the other hand fixed costs remains constant with changes in distances traversed but reduce on a per km basis as number of kilometers increase.