Cash Cycle and Cash Turnovers
Cash Cycle refers to the amount of time which elapses from the point whenever the firms create a cash outlay to purchase raw materials to the point while cash is collected from the sale of finished goods produced by those raw materials.
Cash turnover on another hand refers to the frequency of a firm's cash cycle throughout a year.
Example
XYZ Ltd. currently purchases all its raw materials at credit and sells its merchandise at credit. The credit terms extended to the firm currently needs payment throughout thirty days of a purchase whilst the firm currently needs its customers to pay throughout sixty days of a sale. Conversely, the firm on average takes of 35 days to pay its accounts payable and the average collection period is of 70 days. On average, of 85 days elapse among the point a raw material is purchased and the point the ended goods are sold.
Required
Find out the cash conversion cycle and the cash turnover.
Solution
The following chart can assist further understand the problem:
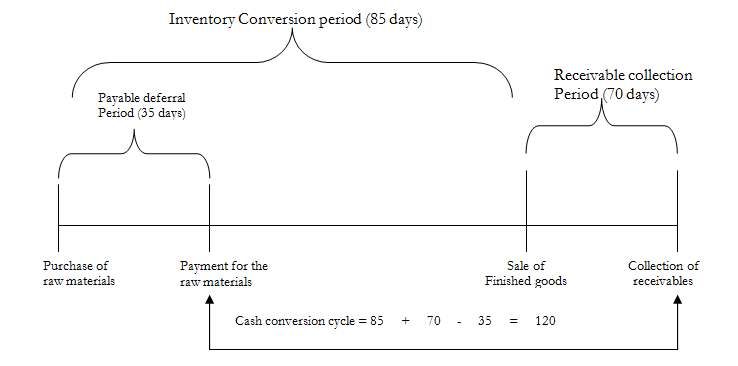
The cash conversion cycle is provided in the following formula as:
Cash conversion = Inventory conversion + Receivable collection - Payable deferral
Cycle period period period
For our example:
Cash conversion cycle = 85 + 70 - 35 = 120 days
Cash turnover = 360 / Cash conversion cycle
= 360/120
= 3 times
Note that cash also conversion cycle can be specified by the following formulae as:
Cash conversion cycle = 360 [(inventory/cost of sales) + (receivable / sales) - ((payable + accruals)/cash operating expenses)]