Q. Make a BST for the given sequence of numbers.
45,32,90,34,68,72,15,24,30,66,11,50,10 Traverse the BST formed in Pre- order, Inorder and Postorder.
Ans:
The property which makes a binary tree into a binary search tree is that for each and every node, X, in the tree, values of all the keys in the left subtree are smaller than the key value in X, and values of all the keys in the right subtree are greater than the key value in X.
The Binary Search Tree for given data 45, 32, 90, 34, 68, 72, 15, 24, 30, 66, 11,
50, 10 is as follows:
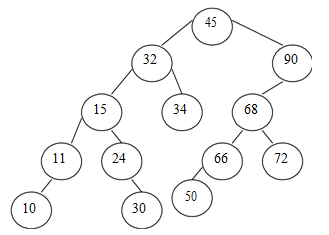
The traversals for the tree shown above is as follows: - Pre-order traversal is- 45 , 32, 15, 11, 10, 24, 30, 34, 90, 68, 66, 50, 72
Inorder traversal given as follows:-
10, 11, 15, 24, 30, 32, 34, 45, 50, 66, 68, 72, 90
Postorder traversal is given as follows:-
10, 11, 30, 24, 15, 34, 32, 50, 66, 72, 68, 90, 45