The boron trihalides are highly volatile; BF3 (b. p., 173 K) and BCI3, (b. p., 260.5 K are gases, BBr3 a volatile liquid (b. p., 319 K) and Bl3 a low melting solid (m. p., 323 K). Boron halides are all hydrolysed by water giving H3B03, and hydrohalic acids, HX or hydrofluoboric acid, HBF4:
Bx3+ 3H2O-------------------------------->H3B03 + 3HX, (X = CI, Br, I)
4BF3 + 3H20-------------------------------> H3BO3 + 3HBF4
In addition to the trihalides, boron forms lower halides of formula, B2X4. But only B2F4 and B2Cl4 have been studied in some detail. B2F4 is a colourless gas whereas 'B2Cl4 is a colourless liquid at room temperature. These halides are much less stable than the corresponding trihalides. B2F4 is the most stable of all the B2X4 compounds. These are spontaneously inflammable in air and react with H2, H20, ROH, CI2, etc.
Unlike BH3 which is unstable, boron trihalides are monomeric molecular compounds and have no tendency to dime rise. In this respect boron trihalides resemble organoboranes, BR3, but differ from diborane, B2,H6, and the aluminium halides, AI2X,. Thus, boron trihalides having three electron pair B2-X6 bonds are electron deficient. However, the interatomic distances, B-X, are substantially shorter than those expected for single bonds. For example, the B-F2 bond length in BF3 is 130 pm which is shorter than the sum of the covalent radii of B (80 pm) and F (72 pm). This shortening of bonds has been explained in terms of appreciable p?-p? bonding
Between an empty p orbital of the sp2 hybridised boron atom and filled p orbitals of one of the fluorine atoms.
All the four trihalides are trigonal planar molecules. This can be explained on the basis of sp2 hybridisation of the boron atom.
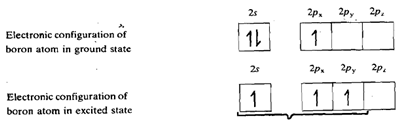
The three hybrid orbitals of boron overlap with singly filled 2p orbitals of three halogen atoms giving rise to three B-X bonds. The empty 2p orbital of boron which is not involved in hybridisation in perpendicular to the plane of the triangle. Its energy is comparable to that of the filled 2p orbitals of halogen atom. Thus it can accept a pair of electrons from a filled 2p orbital of any one of the three halogen atoms, forming a dative ? bond. This makes an octet of electrons around the boron atom. The Bx3 molecule exists as a resonance hybrid of the following three structures as shown in
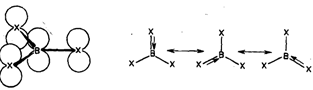
Because of lack of efficient overlapping, the extent of ? bonding decreases as the size of atoms involved in bonding increases. Thus, the extent of ? bonding in boron halides decreases from BF3, to BI3.