A characteristic feature of the transition metals is their ability to form a group of compounds called coordination compounds, complex compounds, or sometimes simply complexes. A typical coordination compound is the intensely blue solid substance Cu(NH3)4SO4 which can be crystallized from solutions of CuSO4 to which a very large excess of concentrated NH3 has been added. These crystals contain two polyatomic ions, one of which is the sulfate ion, SO42–, and the other of which is the complex ion Cu(NH3)42+ which is responsible for the blue color.
We can regard a complex ion such as Cu(NH3)42+ as being the result of the interaction of :NH3 acting as a Lewis base with the Cu2+ ion acting as a Lewis acid. Each NH3 molecule can be considered as donating a pair of electrons to a central Cu2+, thus forming four coordinate covalent bonds to it:
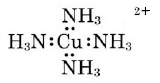
Most coordination compounds contain a complex ion similar to Cu(NH3)42+. This ion can be either positively charged like Cr(H3O)63+, or it can be negatively charged like CoCl63–. Neutral complexes like Pt(NH3)2Cl2 are also known. All these species contain a central metal ion attached by coordinate covalent bonds to several ligands. These ligands are invariably Lewis bases. Some typical examples of ligands are H2O, NH3, Cl–, OH–, CN–, Br–, and SCN–. The number of ligands attached to the central metal ion is said to be its coordination number and is usually 2, 4, or 6. The group of ligands bonded to the metal taken collectively is said to constitute the metal’s coordination sphere.
When writing the formula of a coordination compound containing complex ions, square brackets are usually used to enclose the coordination sphere. Examples are
[Cu(NH3)4]SO4 [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3 [Pt(NH3)2Cl2]
[Cu(NH3)4](NO3)2 K3[Fe(CN)6] [Pt(NH3)4][PtCl4]
When such compounds are dissolved in H2O, each of the ions present in the solid becomes an independent species with its own chemical and physical properties. Thus, when 1 mol [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3 crystal is dissolved in H2O the solution contains 1 mol Cr(H2O)63+ ion which can be recognized by its characteristic grayish-violet color and 3 mol Cl– which can be detected by the precipitate of AgCl which forms when AgNO3 is added to the solution.
Observations on Complex Compounds Containing PtCl2, NH3, and KCl.
| Compound |
Molar Conductivity/
A V-1 dm2 mol-1
|
Moles AgCl
Precipitated per
Mole Compound
|
Electrode to which
Pt Migrates During Electrolysis
|
| 1. [Pt(NH3)4]Cl2 |
3.0 |
2 immediately |
Cathode |
| 2. [Pt(NH3)3Cl]Cl |
1.2 |
1 immediately; 1 after several hours |
Cathode |
| 3. Pt(NH3)2Cl2 |
~ 0 |
2 after several hours |
Does not migrate |
| 4. K[Pt(NH3)Cl3] |
1.1 |
3 after several hours |
Anode |
| 5. K2[PtCl4] |
2.8 |
4 after several hours |
Anode |
An even better example of how the various ions in a coordination compound can behave independently when dissolved in water is provided by the set of Pt(II) complexes shown in the table. The first of these compounds contains the complex ion [Pt(NH3)4]2+ and in each subsequent compound one of the NH3 ligands in the coordination sphere of the Pt is replaced by a Cl– ligand. As a result each compound contains a Pt complex of different composition and also of different charge, and when dissolved in H2O, it shows just the conductivity and other properties we would expect from the given formula. When 1 mol [Pt(NH3)3Cl]Cl is dissolved in H2O, it furnishes 1 mol Pt(NH3)3Cl+ ions and 1 mol Cl– ions. The strongest evidence for this is the molar conductivity of the salt (1.2 A V–1 dm2 mol–1), which is very similar to that of other electrolytes like NaCl (1.3 A V–1 dm2 mol–1) which also yield a +1 ion and a –1 ion in solution, but very different from that of electrolytes like MgCl2 (2.5 A V–1 dm2 mol–1) which yield one + 2 ion and two –1 ions in solution. The conductivity behavior also suggests that the Pt atom is part of a cation, since the Pt moves toward the cathode during electrolysis. The addition of AgNO3 to the solution serves to confirm this picture. One mol AgCl is precipitated immediately, showing 1 mol free Cl– ions. After a few hours a further mole of AgCl is precipitated, the Cl– this time originating from the coordination sphere of the Pt atom due to the slow reaction
[Pt(NH3)3Cl]+(aq) + Ag+(aq) + H2O → [Pt(NH3)3H2O]2+(aq) + AgCl(s)
t is worth noting that in all these compounds, Pt has an oxidation number of + 2. Thus the combination of Pt with one NH3 ligand and three Cl– ligands yields an overall charge of 2(for Pt) – 3(for Cl) + 0(for NH3) = –1. The ion is thus the anion [PtNH3Cl3]– found in compound 4