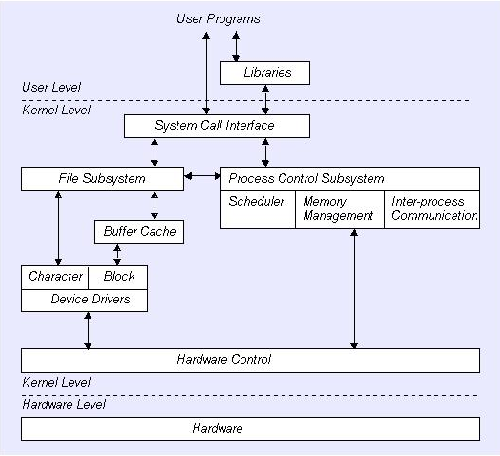
When a computer is started on, the program that executed first is named the ''operating system.'' It controls pretty much all applications in the computer. This adds who logs in, how disks are consumed, how memory is accessed, how the CPU is used.
The way that applications talk to the operating system is via ''system calls.'' A system call seems like a procedure call, but it's not same -- it is a request to the operating system to operate some application.
There are 5 basic system calls that Unix gives for file I/O.
1. int open(char *path, int flags [ , int mode ] );
2. int close(int fd);
3. int read(int fd, char *buf, int size);
4. int write(int fd, char *buf, int size);
5. off_t lseek(int fd, off_t offset, int whence);
The reason the operating system operates I/O is for safety -- the computer has to ensure that if my program has a exception in it, then it doesn't affect the system, and it doesn't collide other people's applications that can be running at later or the same time. Whenever you do screen or disk or network I/O, you have to go through the operating system and use system calls.