Reference no: EM13722389
Question 1: If there is no net force (ΣF→ = 0) acting on an object:
A. it must be at rest
B. it must be decelerating
C. it must be falling with an acceleration of 9.8 m/s2
D. then there must be no forces acting on it at all
E. it must either be at rest or moving in a straight line at constant speed
Question 2: A spelunker (cave explorer) is being lowered on a rope vertically in a straight line and at constant speed into a deep cave opening, which is the appropriate conclusion about the net force (SF) acting on the climber
A. The net force (ΣF→) applied to her must be greater than her weight
B. The net force (ΣF→) applied to her must be equal to her weight.
C. The net force (ΣF→) applied to her must be less than her weight but more than 0.
D. The net force (ΣF→) applied to her must be 9.8 N/kg
E. The net force (ΣF→) applied to her must be 0.
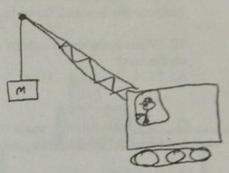
Question 3: A crane at a Seattle shipyard is raising a 650 kg crate into the air to place it on a ship, as shown in the diagram. As it nears the height at which it will be loaded, the crane operator decelerates the crate. A gauge in the crane shows that the rate of deceleration is 1.2 m/s2. What is the tension in the crane cable?
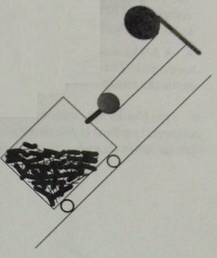
Questions 4: Two boxes are attached to each other by a rope that runs over an ideal pulley, as shown in the diagram. The larger box on the incline has a mass of 7 kg and the smaller hanging box has a mass of 2 kg. The incline is 25° above the horizontal. There is friction between the larger box and the surface of the incline. At the moment shown, the larger box is sliding down the incline and accelerating at 0.75 m/s2.
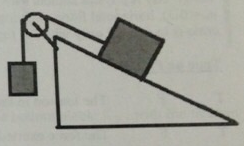
a) The tension in the rope joining the two boxes is:
b) For this situation we can conclude that ft. N, and pk. the friction and normal components of the force exerted by the ramp on the larger box and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and the ramp are related by:
Question 5: A small Smart® car (m-400 kg) is pushing a large Hummer® (2000 kg) up a hill. The two vehicles are in contact with each other at their bumpers. Which of the following statements is true?
A. The Hummer exerts a contact force on the Smart car, but the Smart car doesn't exert a contact force on the Hummer
B. The Smart car exerts a larger magnitude contact force on the Hummer than the Hummer exerts on the Smart car.
C. The Hummer exerts a contact force on the Smart car that is the same magnitude as the contact force the Smart car exerts on the Hummer.
D. The Hummer exerts a larger magnitude contact force on the Smart car than the Smart car exerts on the Hummer
E. The Smart car exerts a contact force on the Hummer, but the Hummer doesn't exert a contact force on the Smart car
Question 6: A bowling ball is rolling down a lane at constant speed in a bowling alley. Which of the following statements is true?
A. The earth exerts a gravitational force on the bowling ball but the bowling does not exert a gravitational force on the earth.
B. The earth exerts a larger magnitude gravitational force on the bowling ball than the gravitational force the bowling ball exerts on the earth.
C. The bowling ball exerts a larger magnitude gravitational force on the earth than the titan the gravitational force the earth exerts on the bowling ball
D. Neither the bowling ball nor the earth exerts a gravitational force on each other because they are in motion with respect to each other.
E. The gravitational force that the earth exerts on the bowling ball and the gravitational force that the bowling ball exerts on the earth are a "Newton's 3`d Law pair" and so they are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction
Questions 7: A worker is attempting to pull a 38 kg wood crate, initially at rest, across a horizontal steel surface (the coefficient of static friction for wood on the steel surface is µs = 0.35 and the coefficient of kinetic friction for wood on the steel surface is µk =0.25) by a rope that is in a horizontal orientation, as shown in the diagram.
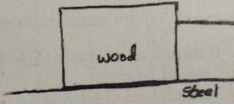
a) What minimum tension does the worker need to apply to the rope in order to initiate motion of the crate?
b) Once the crate is moving, in order for it to continue moving at constant speed the worker will need to apply what tension to the rope?
Questions 8: A box with mass 8 kg is at rest on an inclined surface that makes an angle θ = 12° with respect to horizontal, as shown in the diagram. The coefficient of static friction between the box and the surface is 0.30.
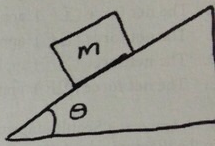
a) What is the magnitude of the friction component of the contact force exerted by the surface on the box?
b) At what minimum angle of the incline will the box begin sliding down the ramp?
Question 9: A physics student uses a taut rope to pull a heavy wood crate along a wood (there is friction: µk = 0.2, µs = 0.3), horizontal floor. The rope is horizontal. The student is pulling the crate at constant speed in a straight line. The crate is in contact only with the rope and the floor.
True or False
T F The tension in the rope is greater than the weight of the crate.
T F The force exerted by the rope should not be included in a free body diagram of the crate since the crate is moving at constant speed
T F The vertical component of the acceleration of the crate is 0.
T F The normal component of the contact force exerted on the crate by the floor is equal to 0.3 times the weight of this crate
T F The friction component of the contact force exerted on the crate by the floor is equal in magnitude to the tension in the rope
T F The magnitude of the contact force that the floor exerts on the crate is 0.2 times the magnitude of the contact force that the crate exerts on the floor
Question 10: A loaded coal cart is being winched up a straight incline at constants speed. The incline makes an angle of 57o with respect to the horizontal. The winch spool has a radius of 0.31 m and an angular speed of 20 rpm. The cart rolls on two steel wheels and the coefficient of friction between the wheels and the incline is 0.033. The cart has an empty mass of 420 kg and it is loaded with 280 kg of coal. The coal cart is located in a very deep mine on the planet Gewurzmuniner IIIB where the value of g is only 71% of its value at the surface of the earth. Find the net force (ΣF→) acting on the coal cart, showing how you obtained your answer using Newton's Laws of motion.
Questions 11: A small block (m1=1.0 kg) is on top of a larger block (m2 = 2.0 kg) and the two blocks are accelerated to the right at 1.6 m/s2 on a horizontal table using a horizontal string attached to the bottom block, as shown in the diagram. There is friction between the bottom block and the table on which the larger block is sliding. The top block is not slipping on the bottom block and so both blocks are accelerating to the right with the same acceleration.
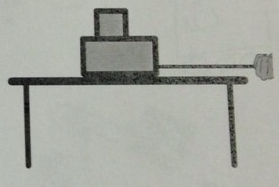
a) The magnitude of the net force (ΣF→) acting on the top block is:
b) The magnitude of the net force (ΣF→) acting on the bottom block is:
c) In comparing the friction component of the contact force acting between the top block and the bottom block, ftop , with the tension in the string, T, we can conclude:
A. ftop > T
B. ftop = T
C. ftop < T
D. ftop = 0 E. T=0
d) Draw a complete free-body diagram of JUST the top block. Make sure to be very careful with the directions of the forces you identify in your free-body diagram.
e) Draw a complete free-body diagram of JUST the bottom block. Make sure to be very careful with the directions) of the forces you identify in your free-body diagram.
Question 12: A 3.0 kg steel block is released from rest and slides down a long plastic ramp that is inclined at an angle of 30° above the horizontal. The coefficient of kinetic friction, µk, for steel in contact with plastic is 0.20. What is the acceleration of the block down the ramp and for what angle of the ramp would it slide at constant speed down the ramp?