Reference no: EM13495350
Part -1:
1. The figure below shows two sample points in a process line.
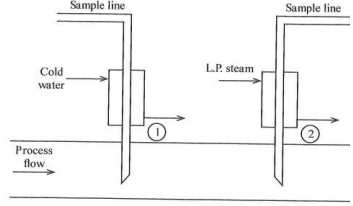
(a) What is the nature of the process fluid?
(b) What are the objectives of the two sample points and in what way do the samples reaching the instruments differ?
(c) Could the effectiveness of the second sample probe be improved and if so how?
(d) What additional feature would be necessary for the second sample line and why?
Before deciding on a pump to supply a sample, what information must be collected and why?
(a) For what purposes is it important to obtain a rapid response to changes in process stream composition and what methods are used, when designing a sample system, to achieve this?
(b) In the same situations as in (a) above, it is also essential to provide analyser systems which do not break down and which maintain their calibration.
What steps should be taken when designing the sampling system and the installation generally in order to ensure this?
4. (a) An X-ray fluorescence analyser requires a sample consisting of a thin layer of powder on a small conveyor belt. The material to be measured consists of a very large flow of solids of widely variable size and it is not certain that large and small pieces have the same composition. The material is also often damp, but the water content is of no interest. The material is transported on a large conveyor and finally dropped into a bunker off the end of the conveyor. Changes in composition are slow, so intermittent sampling can be used.
Explain, with diagrams as necessary, how you would supply a representative sample to the instrument.
(b) In the above example, how often would the sample have to be taken?
(c) If the objective was to determine the average value of the material in the bunker, how could this be done by making one measurement?
Part -2:
1. (a) Basic physical properties (e.g. density, refractive index and thermal conductivity) can sometimes be useful for analysing the composition of a fluid. In what circumstances can this be done?
(b) What information has to be obtained in order to ensure that the method will be a satisfactory one?
(c) It is proposed to use a katharometer to measure the amount (about 5%) of oxygen in nitrogen, in the presence of a small amount (0.5%) hydrogen. How constant would the proportion of hydrogen have to be in order to limit errors in measurement of % oxygen to ± 0.1%?
The thermal conductivities are:
|
nitrogen
|
0.993
|
|
oxygen
|
1.052
|
|
hydrogen
|
6.993
|
(d) FIGURE 1 shows a lcatharometer which allows the use of a reference gas.
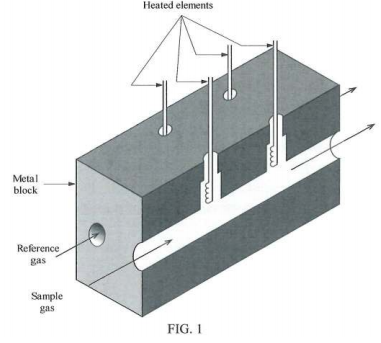
How could this be used to measure the effectiveness of a chemical process designed to remove one of the components from a gas mixture?
2. (a) A measure of refractive index can be used to determine changes in composition of a fluid. Define what is meant by refractive index, and give the relationship between the incident and refracted rays.
(b) A ray of light passes through a material of refractive index 1.5 and then meets material of refractive index 1.3. What is the angle of refraction at the interface between the two materials when the angle of incidence is:
(i) 30°
(ii) 65°?
(c) It is sometimes necessary to measure the refractive index of a fluid which does not transmit light well, or has gas or solids entrained. Describe a method which can be used.
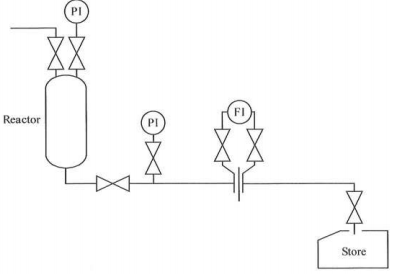
3. (a) On an existing plant, the manager decides that he must know the density of the liquid flowing in part of it; he wishes to use the measurement as a guide to the composition of the liquid. For economic reasons, the plant cannot be shut down. What possibilities are open to him, and what measurements other than density would have to be made; why would they be required and how would the measurements be done?
A diagram of the relevant part of the plant is as shown in FIGURE 2. The density required is of the reactor products; it is not possible to get at the point where it enters the storage tank to draw off a sample.
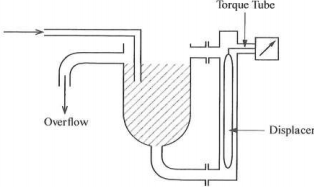
(b) The level of the contents of a vessel are often measured by using a torque tube with the displacer in an external tube which has its top connection above the maximum level and its lower connection near the bottom. A similar instrument can be used to measure density. FIGURE 3 shows an installation for level. Why would it not be satisfactory for density measurement? If you wished to use this type of instrument how would you install it to give satisfactory measurement?
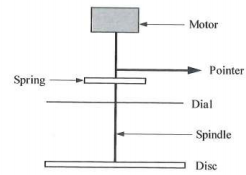
4. (a) Below is a diagram of a rotating disc viscometer (FIGURE 4). Explain its operations and limitations as to use. If, in a similar works situation, it is necessary to make measurements on a non-Newtonian liquid, what would be a better instrument to use and why?
(b) It is intended to automate the operation of an Ostwald capillary viscometer as shown below (FIGURE 5).
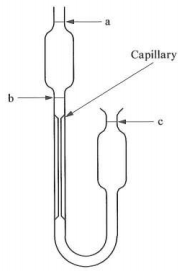
It must be automatically fed with a sample, and then the sample viscosity measured at three different shear rates. What additional equipment would be required? Sketch a typical installation and set out the operational steps.
Part -3:
1. It is necessary to measure the electrical conductivity of a process solution which is prone to deposit on surfaces. Discuss the application and maintenance aspects, with technical explanations and diagrams as necessary, to show how your proposed solution operates.
2. (a) The calibration techniques for cells for measuring conductivity, pH and other ion-selection electrodes are quite different.
Explain these differences.
(b) What is the effect of immersion depth on a glass electrode?
3. What aspects of the design of a pH electrode installation would lead to reduced manual maintenance and improved reliability? Give detailed descriptions of techniques as necessary.
4. (a) An infrared gas analyser has a span of 0 - 1% of the component being measured. It operates at atmospheric pressure and was calibrated when the barometric pressure was 0.995 bar.
The barometric pressure changes to 1.015 bar. What will the
instrument read when the actual percentage of the component is
(i) 0.5%
(ii) 0.8%?
(b) A sample of gas, which is to have one component measured by IR absorption, contains another component whose absorption spectrum seriously overlaps that of the wanted component.
(i) Why might this matter?
(ii) When it does, there are ways of clearing the system to make the measurement possible. Explain these techniques, mentioning any disadvantages.
(c) In an IR gas analyser, a 10 cm tube lets through about 70% (a reduction of 30%) of the radiation absorbed at full scale by the component being measured. Why would a longer tube be better and how much longer would be ideal?
5. (a) What methods are used in infrared, ultravoilet, and visible light systems to reduce the effects of deposition on windows and sample tube walls.
(b) Explain why is it increasingly possible to use mass spectrometry for on-line process applications.
Part -4:
1. Explain why a chromatograph is less suitable than other instruments for direct on-line process control.
What aspects of the design of the measuring and control systems can make on-line control more readily achievable? Give explanations as necessary.
2. (a) Because of its high sensitivity, it is proposed to use an electron-capture detector with a chromatograph column. What special precautions would have to be taken?
(b) Why might an ECD be preferred to a TCD as a detector?
(c) Why is the FID so successful and widely used in the oil and petrochemical industries? What precautions must be taken?
3. (a) FIGURE 1 opposite is a diagram of an oxygen analyser based on the magnetic wind principle. The matched platinum coils wound round the bypass path have two functions. What are they?
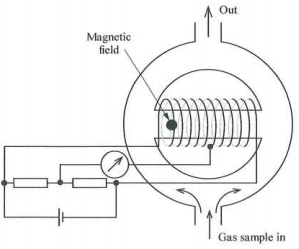
This design is affected by the thermal conductivity of the sample gas. If this is a problem, what alternatives are there, based on the same property of oxygen?
(b) For measuring oxygen dissolved in water, a polarographic cell with silver anode, gold cathodes and KCl electrolyte can be used; in this the current is related to the oxygen reaching the cathode via a membrane. Why is it necessary to renew the electrolyte and the anode? How can this problem be alleviated together with reducing the effects of fouling of the membrane?
4. (a) (i) What is the relative humidity of a gas at the temperature at
which dew starts to form? Explain your answer.
(ii) What would be the R.N. if the temperature were lowered a further 10°C? Explain your answer.
(b) (i) Why is a Peltier effect cooler used in dew-point measuring instruments?
(ii) What is the effect of dust deposits on the mirror in dew-point instruments? What means can be provided to compensate for this effect?
(c) What precautions would have to be taken when measuring free water in a liquid? How would the measurement be made?
5. (a) Power stations are often sited near the coast, which allows them to use sea water for cooling in the condensers at the outlets from their turbines. What analysis measurement would be particularly important in this situation and why? How could the measurement be made?
(b) What methods are used to achieve low levels of corrosion by oxygen in boiler feed water? What measurements are essential to ensure that this is done satisfactorily, and what types of measurement could be used?
(c) The outflow from a works contains organic material. What plant equipment should be included in the effluent stream because of this and why? What must be monitored?
(d) A process vessel has to be shut down in order to do some internal maintenance involving welding. Assuming that it had contained flammable material and that it had been scavenged by a flow of nitrogen followed by air, what measurements would have to be made in order to ensure that the work could proceed safely? Mention any special precautions that would have to be taken.
(e) In a large boiler with several burners, why is it desirable to balance burner performance? What analytical measurements are helpful?
6. Based on your experience, choose an analysis carried out at your workplace. Explain:
(i) what the analysis is
(ii) why the analysis is required
(iii) the method used, together with diagram/description of equipment and process
Part -5:
1. With the aid of a sketch, explain how compensation is achieved in mercury in steel thermometers.
2. A resistance thermometer has a resistance of 117.254 sl at 18°C. If the temperature coefficient of resistance of the resistance thermometer wire is 0.003664 plot a graph of thermometer resistance to a base of temperature over the range 0°C to 100°C and determine :
(i) the fundamental interval of the thermometer
(ii) the resistance at 65°C.
3. With the aid of a circuit diagram(s) show how a manufacturer can avoid the balancing point of a bridge being affected by the high resistance associated with a dirty slidewire contact.
4. (a) The resistance thermometer bridge circuit shown in FIGURE 1 has a designed maximum temperature of 200°C, ignoring the effects of connecting wire resistance. If the connecting loop is 250 m determine the smallest gauge (swg) of copper wire which must be used if the indicated maximum temperature is to be less than 202°C.
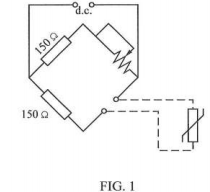
The temperature coefficient of resistance of the thermometer is 0.0042 °C-I and the resistance of the thermometer is 112 C2 at 20°C. Assume the connecting leads are at 20°C.
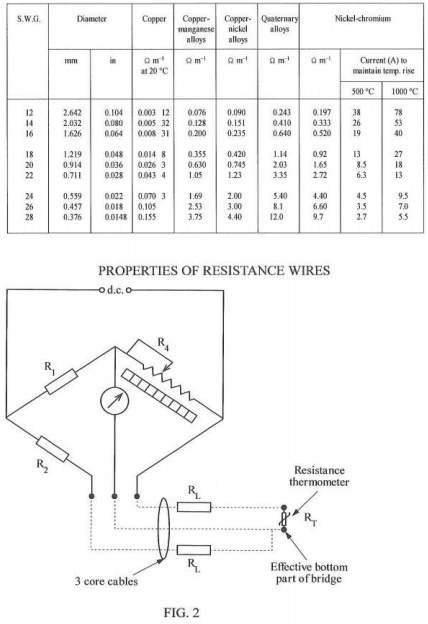
(b) Using the gauge of copper wire calculated in part (a), calculate the maximum indicated temperature using a 3-wire system (as shown in FIGURE 2) over a distance of 125 m.
5. (a) Explain what is meant by 'the law of intermediate metals' relating to temperature measurement using thermocouples.
(b) With the aid of sketches give two industrial situations to which the law in (a) is applicable.
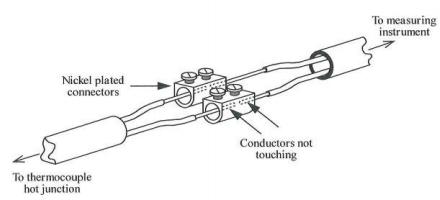
6. A long length of compensating cable is joined as shown in FIGURE 3. The conductors are not touching directly and the connection is made via the connectors themselves. What effect (if any) will the connection have on the accuracy of the system? Give reasons for your answer.
7. (a) With the aid of a sketch describe the construction and principle of operation of a total radiation pyrometer.
(b) Explain how the following parameters affect the total amount of radiation which is emitted from a hot object :
(i) object temperature
(ii) object surface area.
(c) Explain why the emissivity of a black body is equal to I.