Reference no: EM131099932
Question 1. A car initially traveling at 29.2 m/s undergoes a constant negative acceleration of magnitude 1.80 m/s2 after its brakes are applied.
(a) How many revolutions does each tire make before the car comes to a stop, assuming the car does not skid and the tires have radii of 0.305 m?
(b) What is the angular speed of the wheels when the car has traveled half the total distance? rad/s
Question 2.
A sample of blood is placed in a centrifuge of radius 10.0 cm. The mass of a red blood cell is 3.0 ? 10-16 kg, and the magnitude of the force acting on it as it settles out of the plasma is 4.0 ? 10-11 N.
At how many revolutions per second should the centrifuge be operated? rev/s
Question 3. A satellite has a mass of 559 kg and is located at 1.96 ? 106 m above the surface of Earth.
(a) What is the potential energy associated with the satellite at this location?
(b) What is the magnitude of the gravitational force on the satellite?
Question 4. A roller-coaster vehicle has a mass of 590 kg when fully loaded with passengers (see figure).
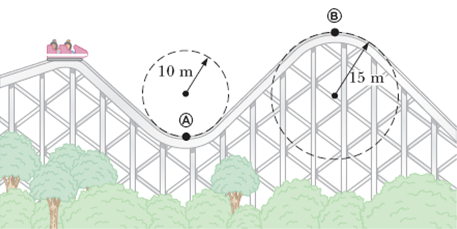
(a) If the vehicle has a speed of 21.0 m/s at point , what is the force of the track on the vehicle at this point?
(b) What is the maximum speed the vehicle can have at point in order for gravity to hold it on the track? m/s
Question 6. A 698-kg satellite is in a circular orbit about Earth at a height above Earth equal to Earth's mean radius.
(a) Find the satellite's orbital speed. m/s
(b) Find the period of its revolution. h
(c) Find the gravitational force acting on it. N
Question 7. A satellite of Mars, called Phobos, has an orbital radius of 9.4 ? 106 m and a period of 2.8 ? 104 s. Assuming the orbit is circular, determine the mass of Mars.
Kg
Question 8.
After the Sun exhausts its nuclear fuel, its ultimate fate may be to collapse to a white dwarf state. In this state, it would have approximately the same mass as it has now, but its radius would be equal to the radius of the Earth.
(a) Calculate the average density of the white dwarf. kg/m3
(b) Calculate the surface free-fall acceleration. m/s2
(c) Calculate the gravitational potential energy associated with a 2.12-kg object at the surface of the white dwarf.
Question 9. A solid, uniform disk of radius 0.250 m and mass 60.7 kg rolls down a ramp of length 5.40 m that makes an angle of 17.0° with the horizontal. The disk starts from rest from the top of the ramp.
(a) Find the speed of the disk's center of mass when it reaches the bottom of the ramp.
(b) Find the angular speed of the disk at the bottom of the ramp.
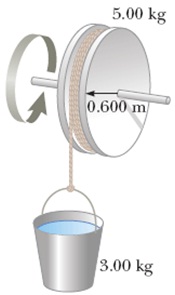
Question 10
Use conservation of energy to determine the angular speed of the spool shown in the figure below after the 3.00-kg bucket has fallen 4.70 m, starting from rest. The light string attached to the bucket is wrapped around the spool and does not slip as it unwinds. rad/s
Question 11.
Four objects-a hoop, a solid cylinder, a solid sphere, and a thin, spherical shell-each have a mass of 5.28 kg and a radius of 0.243 m.
(a) Find the moment of inertia for each object as it rotates about the axes shown in this table.
hoop kg - m2
solid cylinder kg - m2
solid sphere kg - m2
thin, spherical shell kg - m2
(b) Suppose each object is rolled down a ramp. Rank the translational speed of each object from highest to lowest.
solid cylinder > thin spherical shell > solid sphere > hoop
solid sphere > solid cylinder > thin spherical shell > hoop
hoop > solid cylinder > solid sphere > thin spherical shell
thin spherical shell > solid sphere > solid cylinder > hoop
(c) Rank the objects' rotational kinetic energies from highest to lowest as the objects roll down the ramp.
solid cylinder > thin spherical shell > solid sphere > hoop
hoop > thin spherical shell > solid cylinder > solid sphere
hoop > solid cylinder > solid sphere > thin spherical shell
thin spherical shell > solid sphere > solid cylinder > hoop
b) Suppose each object is rolled down a ramp. Rank the translational speed of each object from highest to lowest.
solid cylinder > thin spherical shell > solid sphere > hoop
solid sphere > solid cylinder > thin spherical shell > hoop
hoop > solid cylinder > solid sphere > thin spherical shell
thin spherical shell > solid sphere > solid cylinder > hoop
(c) Rank the objects' rotational kinetic energies from highest to lowest as the objects roll down the ramp.
solid cylinder > thin spherical shell > solid sphere > hoop
hoop > thin spherical shell > solid cylinder > solid sphere
hoop > solid cylinder > solid sphere > thin spherical shell
thin spherical shell > solid sphere > solid cylinder > hoop
b) Suppose each object is rolled down a ramp. Rank the translational speed of each object from highest to lowest.
solid cylinder > thin spherical shell > solid sphere > hoop
solid sphere > solid cylinder > thin spherical shell > hoop
hoop > solid cylinder > solid sphere > thin spherical shell
thin spherical shell > solid sphere > solid cylinder > hoop
(c) Rank the objects' rotational kinetic energies from highest to lowest as the objects roll down the ramp.
solid cylinder > thin spherical shell > solid sphere > hoop
hoop > thin spherical shell > solid cylinder > solid sphere
hoop > solid cylinder > solid sphere > thin spherical shell
thin spherical shell > solid sphere > solid cylinder > hoop
Please write these out clearly so I know which order you chose for each one
Question 12
A large grinding wheel in the shape of a solid cylinder of radius 0.330 m is free to rotate on a frictionless, vertical axle. A constant tangential force of 260 N applied to its edge causes the wheel to have an angular acceleration of 0.852 rad/s2.
(a) What is the moment of inertia of the wheel? kg - m2
(b) What is the mass of the wheel? kg
(c) If the wheel starts from rest, what is its angular velocity after 4.60 s have elapsed, assuming the force is acting during that time?
rad/s
Question 13 Consider the following mass distribution where the x- and y-coordinates are given in meters: 5.0 kg at (0.0, 0.0) m, 3.2 kg at (0.0, 4.7) m, and 4.0 kg at (3.4, 0.0) m. Where should a fourth object of 8.6 kg be placed so that the center of gravity of the four-object arrangement will be at (0.0, 0.0) m?
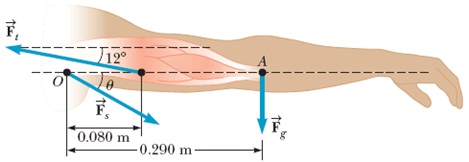
Question 14. The arm in the figure below weighs 44.8 N. The force of gravity acting on the arm acts through point A. Determine the magnitudes of the tension force
F → t
in the deltoid muscle and the force
F → s
exerted by the shoulder on the humerus (upper-arm bone) to hold the arm in the position shown. (Enter your answers to at least the nearest newton.)
Ft = N
Fs = N
Question 15.
Four objects are held in position at the corners of a rectangle by light rods as shown in the figure below. (The mass values are given in the table.)
|
m1 (kg)
|
m2 (kg)
|
m3 (kg)
|
m4 (kg)
|
|
2.50
|
1.50
|
3.50
|
2.10
|
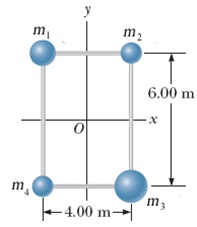
(a) Find the moment of inertia of the system about the x-axis. kg - m2
(b) Find the moment of inertia of the system about the y-axis. kg - m2
(c) Find the moment of inertia of the system about an axis through O and perpendicular to the page. kg - m2
Question 16
A uniform 35.5-kg beam of length
l = 4.95 m
is supported by a vertical rope located
d = 1.20 m
from its left end as in the figure below. The right end of the beam is supported by a vertical column.
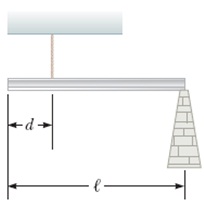
(a) Find the tension in the rope. N
(b) Find the force that the column exerts on the right end of the beam. (Enter the magnitude.) N
Question 17
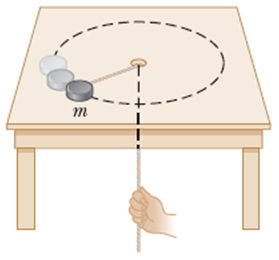
The puck in the figure below has a mass of 0.146 kg. Its original distance from the center of rotation is 40.0 cm, and it moves with a speed of 75.0 cm/s. The string is pulled downward 15.0 cm through the hole in the frictionless table. Determine the work done on the puck. Hint: Consider the change in kinetic energy of the puck. J
Question 18
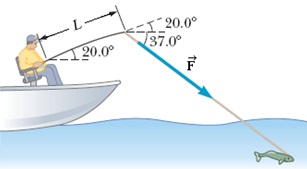
The fishing pole in the figure below makes an angle of 20.0° with the horizontal. What is the magnitude of the torque exerted by the fish about an axis perpendicular to the page and passing through the angler's hand if the fish pulls on the fishing line with a force
F = 118 N at an angle 37.0° below the horizontal? The force is applied at a point
L = 1.97 m from the angler's hands.
N - m
Question 19
A window washer is standing on a scaffold supported by a vertical rope at each end. The scaffold weighs 198 N and is 3.4 m long. What is the tension in each rope when the 692-N worker stands 1.18 m from one end?
a. smaller tension N
b. larger tension N