Reference no: EM132808850
HI5003 Economics for Business - Holmes Institute
Learning Outcome 1: Acquire a broad understanding of the principles of macro and microeconomics in an economy.
Learning Outcome 2: Analyse economic environment nationally and internationally and its influence on business and national economic performance.
Learning Outcome 3: Critically analyse governments fiscal and monetary policy and how they influence the economy and business in general.
Learning Outcome 4: Comprehend how economies benefit from business.
Learning Outcome 5: Synthesise theoretical and practical knowledge of economics, a well-developed understanding of the language of economics and the tools of economics used by policy makers within or outside the country.
Demand and Supply, and Elasticity
Question 1
Due to inflation in Australia in December 2019, the price for petrol increased from AUD
1.35 to AUD 1.45. This caused petrol consumption to decrease from 2500 litres to 2450 litres at a 7-Eleven Petrol Station in Sydney.
Also, when the price for Hyundai 7.5kW Inverter Split System Air Conditioner (Reverse Cycle) increased from AUD 950.00 to AUD 990.00; demand for these air conditioners fell from 2500 units to 2000 units.
Following this condition, answer the questions below.
i. Using the mid-point formula calculate the price elasticity of demand for petrol and Hyundai 7.5kW Inverter Split System Air Conditioner (Reverse Cycle).
ii. Is the price elasticity of demand: elastic, unit elastic or inelastic for each commodity (petrol and Hyundai 7.5kW Inverter Split System Air Conditioner (Reverse Cycle)?
iii. Suppose the government decides to increase tax for petrol and Hyundai 7.5kW Inverter Split System Air Conditioner (Reverse Cycle). Use two diagrams to explain the incidence of the tax increase for each commodity.
Question 2
James was a high school teacher earning a net salary of $4500 per month. After working for one year, he quit his job to start his own kiosk business dealing in various consumer goods. In order to learn how to run the business, James enrolled in a TAFE to acquire accounting skills. James' course was for 6 months. James had to pay $3,000 as tuition for the 3 months.
After the training, James borrowed $40,000.00 from his uncle whom he pays 8 percent interest per year.
Also, James withdrew $ 50,000 from his savings account. He had been earning 5 percent interest per year for this account. Further, to start the business James used his own premises given to him by his father.
His father had been receiving $11,000 from rent per year. Finally, to start the business James uses $75,000 he had been given by his father to go on holiday to USA.
James's first year of business can be summarised as follows:
|
Item
|
Amount $
|
|
Revenue- Orange section
|
250,000
|
|
Revenue- Beverages Section
|
180,000
|
|
2 Cashiers expense (wages per worker)
|
(40,000)
|
|
Mid-year revenue
|
100,000
|
|
Truck expense
|
(80,000)
|
|
Manager expense
|
(60,000)
|
|
Milk sales assistant expense
|
(30,000)
|
|
Equipment expense
|
(50,000)
|
|
Motorcycle expense to ease movement in city
|
(30,000)
|
Based on your calculations of accounting profit and economic profit, would you advise James to return to his teaching job or keep his kiost job? Show your work!
Question 3
The graph below represents sales per week of ABC Inc. Ltd, a monopoly multinational enterprise that supplies Hi-tech components. Use the graph to answer the questions that follow.
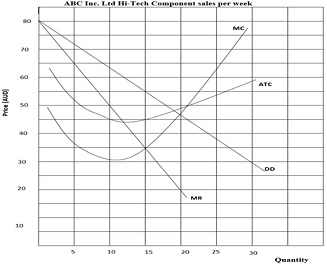
i. State the elasticity of the monopoly firm demand curve.
ii. Considering the figure, examine the benefits of the characteristics of the monopoly demand curve to ABC Inc. Ltd.
iii. Suppose the demand and cost curves result in ABC Inc. Ltd earning an economic profit. Do you think ABC Inc. Ltd firm will earn profit in the long- run? Explain your answer. Assume all factors constant.
iv. Examine the effects of ABC Inc. Ltd on consumers.
Question 4
The table below is extracted from Happy land Republic, Bureau of Statistics records for 2018-2019. Use the information in this table to answer the questions that follow.
|
Item
|
Base year (2015)
|
2016
|
|
Production
|
Price
|
Production
|
Price
|
|
Used car sales
|
5,000
|
2000.00
|
6,000
|
2,500
|
|
Factory components sales
|
8,000
|
500.00
|
10,000
|
1200.00
|
|
Cloth sales
|
8,000
|
20.00
|
14,000
|
35.00
|
|
Beef sales
|
1,500
|
10.00
|
1,800
|
12.00
|
|
Milk litres sales
|
5,000
|
1.30
|
6,000
|
2.50
|
|
Computers sales
|
2000
|
500.00
|
2500
|
800.00
|
|
Printers sales
|
500
|
300.00
|
400
|
355.00
|
|
Raw materials for tractor assembling plant sales
|
4500
|
250.00
|
4450
|
300.00
|
i. Calculate Happy Land Republic's nominal GDP and real GDP in 2016
ii. Why does real GDP always defer from nominal GDP?
Inflation and unemployment, and Macro economics
Question 5
i. Use two diagrams to explain the effects of the determinants of aggregate demand on real GDP in a nation.
ii. Suppose there is an expectation of a rapid general price increase in goods and services in Australia in January 2021. Examine the effects of the anticipated general rapid increase in price for goods and services.
Question 6
The government of Australia has embarked on various policies such as Job Keeper and provision of subsidies to firms in order to reduce the severity of COVID 19 on the economy. Suppose the money supply expands such that the Reserve Bank predicts that the economic expansion is not sustainable.
Use two diagrams one for the money market and another for the goods and services (Aggregate demand and Aggregate Supply model), to explain the policy that the Reserve Bank can adopt in order to overcome the effect of increasing money supply on the economy.
Assume that:
• money supply increased from the equilibrium of AUD 40 billion to AUD 70 billion
• Interest was reduced to interest rate of 1.5% as part of the stimulus package for the nation to overcome the effects of COVID 19. But the equilibrium interest rate is 4%
• Assume that equilibrium real GDP is AUD 60 billion
• Assume that inflation during COVID crisis was at equilibrium price of CPI 65
• Assume that to overcome the inflationary crisis aggregate demand has to reduce by AUD 30 billion.
• Assume to restore the economy to equilibrium inflation has to be adjusted to CPI 120
• This is the completion of the tutorial
Attachment:- Economics for Business.rar