Reference no: EM132534816
MECH2300 Structures and Materials - The University of Queensland
Integrated Assignment
Problem Description
A cage is to be operated in a vertical shaft in an underground mine. The cage lowers and lifts people, equipment or materials from ground level, to an underground, horizontal roadway 200 m below. The maximum load rating of the cage is 45,000 kg. The cage is lowered or lifted by a winch and cable system. The winch is powered by an electrically driven, winding engine located at the ground level. At the bottom of the shaft is a sump which removes water from the lower level of the mine. A sketch of the layout of the shaft is shown in Figure 1.
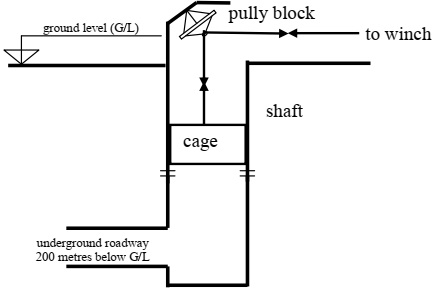
Figure 1. Layout of the people, materials and equipment shaft.
Figure 2 shows a schematic of the pulley block at the top of the cage shaft. The pulley shaft is made of a 6150 alloy steel and the load carrying members are made from a 1020 low carbon steel. Details of the eye bolts, used to attach 1) the members to the rigid plate; and 2) the pully block to the support structure are shown in Fig. 3.
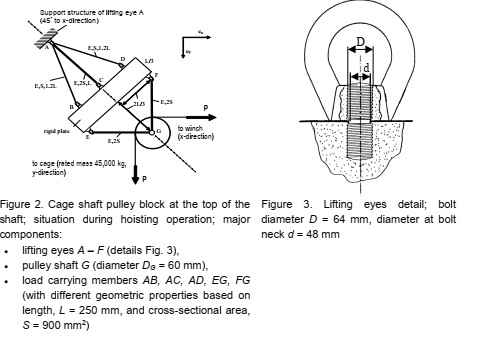
Tasks
In this integrated assignment you will investigate the materials and structural aspects of the pulley block system. Some data for the eye bolt materials is provided in Appendix A.
The specific tasks are:
*Task 1 Calculate the forces and stresses in the axial members, the lifting eye bolts and the pulley shaft (the energy transfer pathway). Discuss the results.
Task 2 (a) Consider the eye bolts in more detail. The bolts are made from a quenched and tempered medium carbon alloy steel, 4340. Most of the material properties can be found in the links in Appendix A. Will any of the eye bolts fail?
(b) One of the eye bolts was not tempered correctly and its mechanical properties are
σY = 2,000 MPa and K1c = 20 MPa.m1/2. Will the structure now fail, if this eye bolt was used in any of the eye bolt positions. If so, what will happen to the structure?
Task 3 The cage will run 20 load cycles per day. In addition, the pulley block regularly experiences temperatures of up to 50°C. Maintenance is very costly to mine sites, as often large pieces of equipment need to be shut down for extended periods. Hence, a full system overhaul with detailed inspection is only planned for every 3 years. You would like to ensure that your eye bolts are safe within the maintenance cycle. You are provided with the choice of one of the following alloys for the eye bolts:
• Quenched & tempered medium carbon alloy steel, 4340;
• Quenched & tempered medium carbon steel, 1045;
• Solution treated & aged Ti-6Al-4V; or
• Cold worked 304 stainless steel.
Taking into account static loads, in addition to long-term effects, such as fatigue and creep, which material is the most appropriate for the eye bolts? Provide a clear comparison and argument for this choice.
For the chosen material and heat/mechanical treatment, describe the microstructural features that impact the yield strength.
*Note: Need only Task 1
Attachment:- Structures and Materials.rar