Reference no: EM13809100
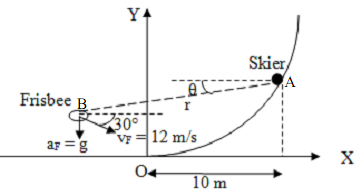
1) A skier A going down the ski slope has a speed of 20 m/s at the instant shown and his speed is increasingly uniformly throughout the path at the rate of 1 m/s2. The ski slope is represented by the path y = x3/20 (x,y in meters, measured from O). The skier observes a Frisbee at point B. The Frisbee, as shown, has a speed of 12 m/s and is falling freely under its own weight (neglect air drag). At the instant shown, the position of the Frisbee with respect to the X-Y coordinate system at O is given by the coordinate (-7.5, 15). For this instant,
i) Find the velocity of Frisbee relative to the skier (i.e. V'B - V'A )
ii) Find the acceleration of the Frisbee relative to the skier (i.e. a'B - a'A )
iii) Compute the values of r', θ', r", θ" for the Frisbee as recorded by the skier. [Hint: Fix polar coordinate system at A, draw er, eθ vectors to B, and make use of your answers from i) and ii) above to get the final answers to this part of the problem]
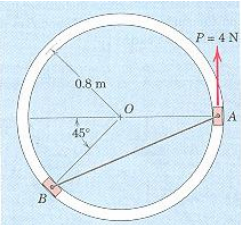
2) The two 0.2 kg sliders A and B move without friction in the horizontal-plane circular slot. Determine the acceleration of each slider and the normal reaction force exerted on each when the system starts from rest in the position shown and is acted upon by the 4-N force P. Also find the tension in the inextensible cord AB.
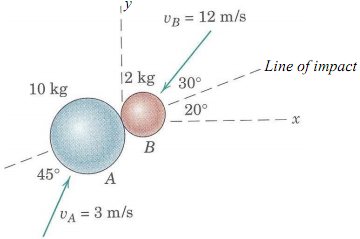
3) The sphere of mass m1 travels with an initial velocity v1 as shown and directly strikes the sphere of mass m2 (initially at rest). For a given coefficient of restitution e, determine the mass ratio m1/m2 which results in m1 being motionless after impact. For this ratio, what is the kinetic energy of m2 after impact?

4) A 150 lb skateboarder starts from rest (at point A) and skates along a parabolic path given by y = x2/4 (x, y in meters). Compute (i) the normal force N on the skier just before he crosses point O (ii) time it took for the skier to reach point O (iii) his speed at the instant he reaches point O. Assume the path is frictionless.
5) Consider a pulley-block system to be attached to an elevator ceiling. The elevator begins to accelerate upwards from its rest configuration with a constant acceleration of aL = 3 m/s2. At this instant, the 60 kg block A is released from rest. If the masses of the pulleys and the cord are neglected, determine the speed of the 40 kg block B in 4 seconds. Also determine the tension in each cable.

6) A small block A of mass m resting on a frictionless tabletop is attached by cables to a point P (see figure below) and, by means of a massless pulley, to a block B of equal mass. Further, the block A is attached to a point O by means of a spring. The undeformed length of the spring is l0 = 0.5 meter and stiffness k = 5mg/l0. The cable PA is cut and the block A starts to move.
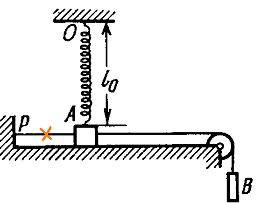
Find the speed of block A when it is breaking off the surface of the tabletop.
7) Consider the following system in a vertical plane.
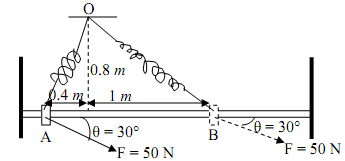
The slider moves from A to B on a frictionless rod under the action of the constant external force F (as shown) [‘constant' means neither magnitude nor direction of F changes]. The slider is initially at rest at point A. The spring is attached to the slider on one end and the fixed point O on the other end. Stiffness of the spring is k = 250 N/m.
The unstretched length of the spring is 0.6 meters. Mass of slider, m = 2 kg
a) Compute the speed of the slider at B
b) Compute the normal force on the slider at point A and point B
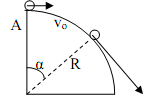
8) Find the angle α at which the particle leaves the circular ramp. Assume the ramp to be frictionless. m = 1kg, vo (initial speed at A) = 1.5 m/s, R = 25 cm. Find the normal force on the particle when the particle is at an angle α/2.
9) A ball is launched from point B on a hill (as shown). Due to windy conditions, the ball experiences wind forces which give it an additional uniform acceleration of 3 m/s2 in the direction shown. Compute how far from point B the ball will hit the hill. Assume hill's slope extends to infinity (in other words, the hill is huge)
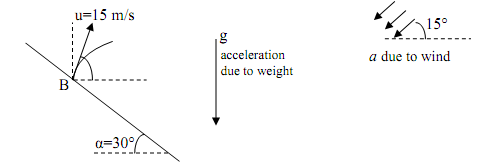
Assuming the coefficient of restitution of impact, e is 0.85, find the rebound velocity of the ball. [Take mass of ball = 0.25 kg]
10) Sphere A collides with sphere B as shown in the figure (next page). If the coefficient of restitution is e = 1, determine the x- and y- components of the velocity of each sphere immediately after impact. Motion is confined to x-y plane. Neglect any friction effects.
Further prove that the kinetic energy of the system (i.e. sphere A + sphere B) is conserved.
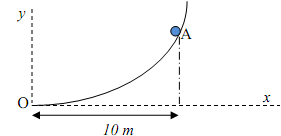
11) Karen, an avid skateboarder, starts from rest at point A and goes along the path, as shown, from point A to point C. AB is a hyperbolic curve given by y = 25/x (x, y in meters). While she is going down the track from A to B, her speed increases uniformly at the rate of 2 m/s2.
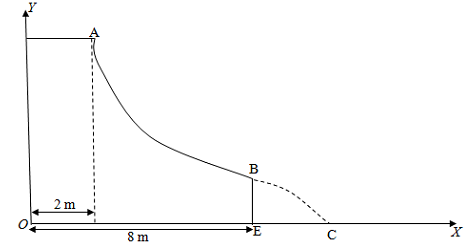
i) How far does she land from the base point E of the track?
ii) How much time does she take to go from A to C?
iii) Compute the magnitude of her total acceleration just before she leaves point B.
[g = 10 m/s2, No drag effects]
The length of the path from A to B is given to be 11.77 m.
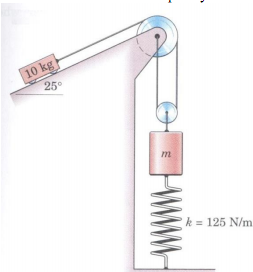
12) The system is released from rest with no slack in the cable and with the spring stretched 200 mm. Determine the distance traveled by the 10 kg cart before it comes to rest if m = 2 kg. Assume no friction and massless pulleys.
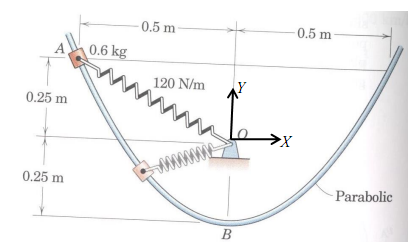
13) The 0.6 kg slider is released from rest at A and slides down a smooth parabolic guide (which lies in a vertical plane). The unstretched length of the spring is 200 mm and its stiffness is 120 N/m. Find the speed at point B and the normal force exerted by the guide onto the slider when it reaches point B. [Hint: Assume the equation of parabola is y = c1x2 + c2, you can get constants c1, c2 from geometry]
14) The 0.5 kg slider moves without friction along the fixed curved rod from A to B in the vertical plane under the action of the constant 20 N tension in the cable. The unstretched length of the spring is 2 m. (Take g = 10 m/s2 ).
a) If the slider is released from rest at A, calculate its speed when it reaches point B.
b) What is the spring force (give both magnitude and direction) at point A and point B?
c) What is the normal force (give both magnitude and direction) from the rod onto the mass at point A and B? Assume B is on the straight portion of the rod.
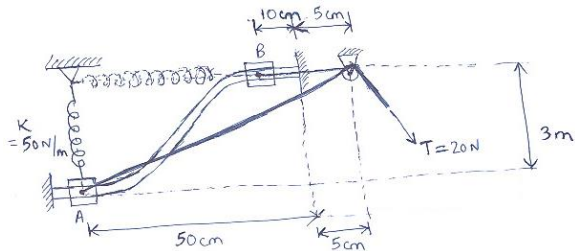
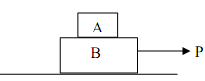
15) Two blocks A and B are pushed up a frictionless inclined plane by an external force F as shown in the figure. The coefficient of friction between the two blocks is μ = 0.2. The masses of the two blocks are mA = 5 kg and mB = 2 kg. Find the magnitude of the maximum allowable force such that no relative slip occurs between the two blocks.
16) A particle moves in a straight line (i.e. the x-axis) with acceleration ⁄ , x is position measured from origin, is the instantaneous speed. It is released at x = 0 with an initial speed of 1 m/s. Find its speed when its position x = 6 m.
17) At the instant shown, a particle moving down on a parabolic path has a speed of 6 m/s at point B and its speed is increasing at a uniform rate of 0.8 m/s2.
i) Express its velocity and acceleration at point B in en-et system
ii) Express its velocity and acceleration at point B in i-j system (origin at O)
iii) Find r', θ', r'', θ'' (as recorded by a stationary observer A) at this instant
iv) Find (as recorded by a stationary observer A) at this instant
The equation of the path with respect to the given XY system is ⁄ (x, y in meters). The origin of the XY system is at point
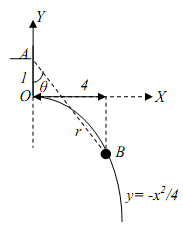
18.
i) A particle moves on a parabola y2 = 8x to point A = (2,4) from point B = (0.5, 2) under the action of a variable force F' = xi + y2j, the magnitude and the direction of this force change with the x-y position of the particle). Find the work done by this force as the particle goes from B to A on the parabolic path
ii) Next, assume the particle takes the path BC (a line) and then CA (another line) under the action of the same force ?F to reach point A starting from point B. Find the total work done by ? ?F n this path.
iii) Can you conclude whether or not the force ?F is conservative?
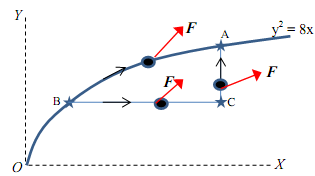
19) Compute the acceleration of the blocks M1, M2
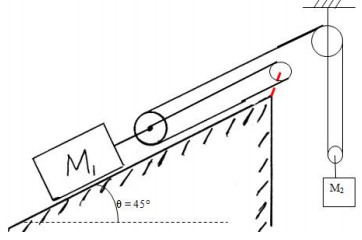
Assume the pulleys are massless and the cables are inextensible. M1 = 30 kg, M2 = 10 kg.
Inclined plane is rough: µs = 0.25, µk = 0.2
20) Blocks A and B weigh 80 lb and 100 lb respectively. Surfaces are rough; for the contact between A and B: µs = 0.2, µk = 0.15, and for the contact between B and ground:
µs = 0.15, µk = 0.1. The blocks are stationary when the constant force P is applied (as shown). Determine accelerations of A and B if (a) P = 25 lb (b) P = 50 lb (c) P = 100 lb.