Reference no: EM13859101
Q1. Thermodynamics deals with a system and its surroundings, which jointly make up the (thermodynamic) universe.
Q2. A system may be a piece of metal. The surroundings are where we stand to make observations of the system and infer its properties.
Q3. A beaker of water immersed in a water bath makes up the (thermodynamic) universe.
Q4. Thermodynamic properties are called extensive when they depend on the quantity of matter in the system.
Q5. Mass, volume, and internal energy are not extensive properties.
Q6. Intensive properties are independent of the amount of matter present in the system.
Q7. Temperature, pressure and density are not intensive properties.
Q8. The specific volume per mole of material is called the molar volume.
Q9. The molar volume of copper (molecular weight = 63.54 g/mol and density Ρ = 8.96 g/cm3) is 7.09 cm3/mol.
Q10. At a phase transition the enthalpy does not vary discontinuously due to the latent heat of the transformation.
Q11. The enthalpy of a homogeneous system is H = S + pV. In this expression H is enthalpy, S is entropy, p is pressure and V is volume.
Q12. The unit of enthalpy is Jmol-1K-1
Q13. The total enthalpy of a system cannot be measured directly. What we measure is the change in enthalpy, ΔH.
Q14. In thermodynamics a change is allowed to occur if as a result of the change dS > 0 (the entropy increases) or ΔG < 0 (the Gibbs free energy decreases)
Q15. The criterion of thermodynamic equilibrium for a system under constant temperature and pressure is that the Gibbs free energy G has reached its minimum possible value
Q16. A thermodynamic change is spontaneous when the change in free energy is negative
Q17. If a material could exist in more than one state, the one with the lower (i.e., more negative) Gibbs free energy would not be the preferred one.
Q18. ΔG > 0 means that work must be done on the system to force it to change (in other words there will be an activation energy barrier)
Q19. ΔG > 0 means the change would not occur spontaneously
Q20. The specific heat cp is a measurable property
Write down what the subscript p means in Cp
Write down an equation for Cp and explain the meaning of symbols used
Q21. The specific heat cp specifies the amount of heat energy required to change the temperature of a material by a given amount.
Q22. The unit of specific heat cp is JK-1 (Write down how you could calculate the change in enthalpy between temperatures T1 and T2 for a pure element with specific heat cp)
Q23. Draw a free energy versus composition diagram for two solid solution phases α and β that are at equilibrium at temperature T1. Show the compositions of the phases at equilibrium.
Q24. Draw a free energy versus composition diagram for temperature T1 for two phases α and γ, where the former is a solid solution and the latter an intermetallic. These phases are at equilibrium at the temperature T1. Show the composition of the α phase in equilibrium with γ of sizes r1 < r2 < r3.
Q25. At the eutectic temperature TE of a binary alloy system A - B, the liquid and solid solution phases α and β co-exist at equilibrium. Draw a schematic free energy versus composition diagram to show this equilibrium at TE. In this diagram show the composition of each phase at equilibrium.
Q26. Solidification is a phase change ........ .......
Q27. Solidification is a diffusion controlled transformation ........ ........
Q28. Solidification is not a nucleation and growth process ........ ........
Q29. Write down the condition for assuming that the free energy driving solidification is proportional to the heat of fusion ........ ........
Q30. In heterogeneous nucleation the presence of catalytic particles ensures that nucleation will occur at lower critical melt undercooling compared with homogeneous nucleation ........ .........
Q31. The presence of nucleating agents affects the size of the critical nucleus
Q32. The unit of nucleation rate is nuclei/sec .......... ........... Draw a schematic diagram to show how nucleation rate depends on melt undercooling
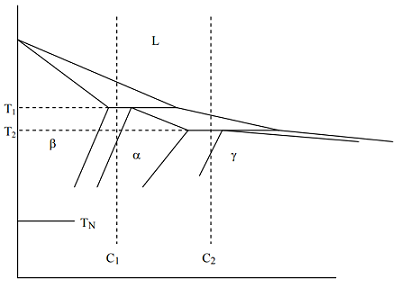
Q33. In the schematic phase diagram below assume that for the alloys of composition C1 and C2 nucleation occurs at the temperature TN.
1. Complete the phase fields and write down the "reactions" at the T1 and T2.
2. For the alloy of composition C1 write down the nucleation undercoolings for the phases α, β, γ and the freezing ranges of α amd γ.
3. For the alloy of composition C2 write down the freezing ranges of the phases β and γ and the nucleation undercoolings for the phases α, β, γ
You might have to use more copies of the schematic phase diagram in order to answer 2 and 3
Q34. The homogeneous nucleation rate can be written as Jhomogeneous = (D Nv/λ 2 ) exp( - ΔG* homogeneous/kT) where D is the atomic diffusion coefficient characteristic for atomic motion necessary for crystallization at temperature T, Nv is the average atomic concentration per unit volume, and λ is the jump distance or mean atomic distance.
Draw a temperature (or undercooling) versus nucleation rate schematic diagram to show how the pre-exponential and exponential terms in above equation for Jhomogeneous vary with temperature (or undercooling).
Briefly explain the shape of the curves
Q35. A dendrite is the growth structure of the solid crystal during solidification that forms from a morphologically unstable S/L interface under typical solidification conditions of an alloy ........ .........
Q36. The solid-liquid interface of an alloy becomes morphologically stable when there is a constitutionally super-cooled region ahead of it ......... .........
Q37. For a given alloy, the critical solid-liquid interface velocity for morphological instability decreases with the temperature gradient in the melt ahead of the interface .......... ..........
Q38. At growth rates (S/L interface velocities) exceeding the absolute stability velocity the S/L interface is dendritic .......... ..........
Q39. In solidification we are concerned only with diffusion in the liquid (melt). ........ .........
Q40. The diffusivity of a solute in a solid is lower than the diffusion in liquid for all substitutional elements by at least a factor of 1000 ........ .........
Q41. In "normal" solidification (i.e., not rapid solidification) there is redistribution of solute at the S/L interface ........ ..........
Q42. In "normal" solidification (i.e., not rapid solidification) the solidification front can be taken to be in local equilibrium between the solid and the melt (corrected for curvature undercooling) ......... ...........
Q43. In rapid solidification (i.e., not "normal" solidification) no local equilibrium is established at the S/L interface ......... ..........
Q44. Rapid solidification is observed in weakly undercooled melts ......... ...........
Q45. The partitioning of solute decreases (i.e., the partition coefficient tends towards one) as VS/L (or RS/L) increases ......... ...........
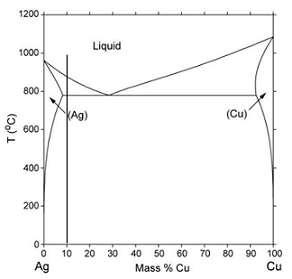
Q46. The equilibrium phase diagram of the binary system Ag-Cu is shown in the figure below.
In the given phase diagram, complete the phase fields and estimate the maximum solid solubility of Cu in Ag and of Ag in Cu.
Consider the alloy Ag-10mass%Cu (shown in the phase diagram). For this alloy estimate the fraction eutectic for solidification under conditions that allow concentration gradients to develop only in the solid phase.
Q47. The Gibbs-Thomson undercooling is attributed to the radius of curvature of the solid-liquid interface ......... ...........
Q48. Particles of very small radii of curvature melt at higher temperature compared with particles of large radii of curvature .......... ...........
Q49. Flat solid-liquid interfaces are formed when a phase has low entropy of fusion. .......... ...........
Q50. The growth of flat solid-liquid interfaces is continuous