Reference no: EM13845698
Problem 1:
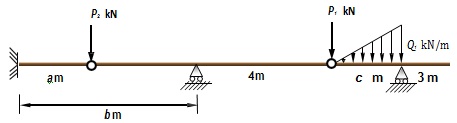
(a) For beam shown in Figure 1, neglect the self-weight of the beam,
(i) Determine the reactions using Spacegass.
(ii) Determine the BMD and SFD using Spacegass.
(iii) Verify your answers for (a)(i) and (ii) using hand calculations.
(b) Include the self-weight of the beam with load case in part (a), what is the difference in displacement if compared with load case in part
(a) at the position where maximum absolute deflection occurs.
(c) Based on the BMD, redraw the deflected shape using free hand for both load cases in part (a) and (b).
Assume that the beam in Figure is 400mm depth * 150mm width concrete section with concrete strength of 25 MPa.
Problem 2:
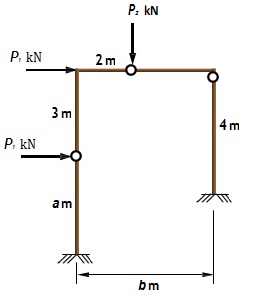
(a) For the frame shown in Figure, determine the reactions and draw the shear force diagram (SFD), bending moment diagram (BMD) and deflected shape for the following load cases using Spacegass. Assume that all members are made of 250UB25.7 (Grade 300 steel). Self- weight can be negligible.
(i) Case 1: P1
(ii) Case 2: P2
(iii) Case 3: P1 + P2
Show the hand calculation for Case 3.
Problem 3:
The beam shown in Figure is subjected to a number of primary loads including:
- G1 = downward uniformly distributed dead load;
- Q1 = downward uniformly distributed live load;
- G2 = downward concentrated dead load
- Wup = uniformly distributed uplift wind load;
The primary loads could occur simultaneously in accordance with the following load combinations for Ultimate Limit State:
- 1.35G
- 1.2G + 1.5Q
- 0.9G + Wup
The load combination for Serviceability Limit States is
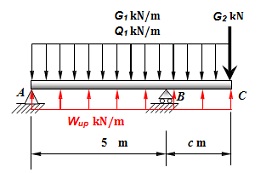
(a) Considering all 4 load combinations above and using Spacegass, determine the maximum and minimum (positive and negative) shear forces, bending moments and deflections of the beam (refer to plots of diagram or text report) should be designed for. Assume that beam is made of 610UB125 Steel. Consider the self-weight of the beam (p/s include SW with G1). Maximum absolute value in each category (Limit States) is considered "Design values".
|
Limit States
|
Load Combinations
|
Shear (kN)
|
Moment (kNm)
|
Deflection (mm)
|
|
Max
|
Min
|
Max
|
Min
|
Max (up)
|
Min (down)
|
|
Ultimate
|
1.35G
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.2G + 1.5Q
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.9G + Wup
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Serviceability
|
G + Q
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Design Values
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(b) For the load combinations producing the maximum shear force and bending moments, double check your Spacegass results using hand calculations.
(c) The maximum allowable deflection (upward or downward) is 30mm. Determine the adequacy of the beam deflection check.
(d) If the beam is oversize with respect to deflection, what is the minimum beam size can be used to fulfill deflection requirement?
Problem 4:
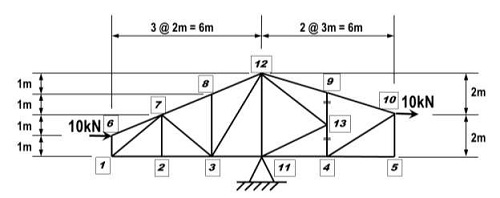
All the members for the truss shown in Figure are pin-connected. The truss is pin supported at node 11. All truss members are made of 125SHS5 steel. Self-weight is negligible.
Locate the roller support at node a, and the downward force 10kN at node b. For this configuration and loads shown:
(a) Use Spacegass to determine all reactions and member forces in the truss. Include graphical outputs from Spacegass showing the member numbers and member forces. Also include a printout of input data and output results.
(b) Use hand calculations to check the reactions and determine the member forces in members 3-12, 4-11 and 12-13 (include in your answers whether the members are in tension or compression).
|
Find the potential energy
: Suppose each red ball weighs 20 lbs. Find the potential energy (PE) for each ball on each ramp. In this lab mass is given in pounds and height is in feet, so use 32.2 ft/sec2 as the gravitational constant. Your answer will be in foot-pounds since ..
|
|
Cypress are the famous timber-yielding plants
: Pine, fir, spruce, cedar, larch and cypress are the famous timber-yielding plants of which several also occur widely in the hilly regions of India. All these belong to
|
|
Case study- lundberg vs church farm inc
: Case Study: Lundberg v. Church Farm, Inc., Court of Appeals of Illinois, 502 N.E.2d 806, 151 Ill.App.3d 452 (1986). Identify the parties that have an interest in the decision and why that matters
|
|
Identify the decision and the legal implications
: Identify the decision and the legal implications. Identify the parties that have an interest in the decision and why that matters. Analyze the possible choices and outcomes of the decisions
|
|
Determine the reactions using spacegass
: (a) For beam shown in Figure 1, neglect the self-weight of the beam, (i) Determine the reactions using Spacegass.
|
|
Discuss one way fungi interact with another organism
: Choose one group of fungi and discuss what makes them unique OR Discuss one way fungi interact with another organism in a parasitic or mutualistic way.
|
|
Domestic and international human resource management
: Discuss the key differences between domestic and international human resource management (HRM). Choose one difference and provide a more detailed and personal opinion about it, including examples of potential issues.
|
|
Explain basic provisions of contract law relative to offer
: Describe the elements of a contract and explain the basic provisions of contract law relative to offer, acceptance, capacity, legality, fraud, third-party rights, performance, and breach of contract
|
|
Differences between best-fit and best-practices perspectives
: Set up a debate: Nonfinancial returns are more important than pay. Contrast the essential differences between the best-fit and best-practices perspectives. Should Bank of America change its compensation strategy to include more subjective assessments..
|