Reference no: EM131667165
Q1. Consider the following ER diagram:
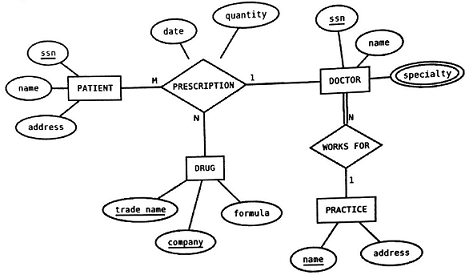
For each claim, state whether it is true or false given the model shown in the diagram. Explain your answers.
(a) Different companies cannot make a drug with the same trade name.
(b) A patient can only be prescribed a particular drug by one doctor.
(c) A patient can be prescribed the same drug by the same doctor on different dates.
(d) A patient can have prescriptions from at most one doctor.
(e) Someone cannot be both a patient and a doctor.
(f) A doctor can have more than one specialty.
(g) More than one patient can have the same name.
(h) A doctor can work for several different practices.
(i) A practice must have at least one doctor working for it.
(j) A patient can locate all of the doctors working in a particular city.
Q2. Consider the following relational schema for a course catalog:
COURSE (Department, CourseNumber, Title, Description, TaughtBy)
PROFESSOR(Department, Name)
- COURSE.TaughtBy refers to PROFESSOR.Name
For each claim, state whether it is true or false given the schema. Explain your answers.
(a) There can be more than one course in the same department.
(b) A course can have more than one title.
(c) Every professor must teach at least one course.
(d) A course can be included in the catalog without the name of the professor teaching it.
(e) A course can be taught by someone not included in the catalog.
(f) There can be several professors with the same name as long as they are in different departments.
Q3. Consider the following ER diagram:

Does the relational schema below accurately express the relationship constraints (cardinality and participation) present in the ER diagram? Explain why or why not.
EMPLOYEE(Ssn, FirstName, LastName)
OFFICE(SranchNumber, City, Ssn)
- OFFICE.Ssn refers to EMPLOYEE.Ssn
Q4. Draw an ER diagram which captures as accurately as possible the following information about the operations of a large real estate rental management company. Include participation, cardinality, and key constraints. If necessary specifics are lacking, make reasonable assumptions and state those assumptions. If there are any elements which cannot be represented in your diagram, identify them and explain what the problem is.
Draw your diagram by hand (neatly) or use a program such as dia.
- The company has branch offices in cities across the US. Each branch office has a unique branch number, an address (with a street, street number, city, state, and zip code), and up to three phone numbers.
- Each branch office has a staff. The data stored for each staff member includes their ID number (unique across all branches), name, address, position, salary, supervisor's name (where applicable), and the branch office where they work. Staff members may be reassigned to different offices, but never work in more than one office at a time.
- One staff member is the office manager.
- Some staff members are supervisors. Only supervisors can supervise other staff members. The date when each supervisor became a supervisor is recorded. Supervisors also get a monthly bonus, the size of which is based on the number of years since they became a supervisor and the number of staff members supervised.
- Each branch office offers a range of properties to rent. The data stored for each property includes the property number (unique to the branch with the listing), address (street, street number, city, state, zip code), type, number of rooms, monthly rent, and owner. The management of a property is assigned to a staff member whenever it rented out or is listed for renting. Properties may be listed in the system even if they are not currently rented or available for rent.
- There are two kinds of property owners, private individuals and businesses. For private individuals, the owner's name, address, and phone number are stored. For businesses, the business name, type of business, address, phone number, and contact name are stored. Both private individuals and businesses are assigned a (globally) unique ID.
- A prospective renter must first register at a particular branch office. For each such client, a client number (unique to the branch where the client is registered) is assigned and the client's number, name, phone number, preferred type(s) of accommodation, and maximum budget are recorded. Also stored are the staff member and branch office that processed the registration and the date the client joined.
- When a property is rented out, a lease is drawn up. The lease includes the lease number (unique to the branch drawing up the lease), client number, client name and address, property number and address, monthly rent, method of payment, amount of the initial deposit paid (if any), duration of the lease (e.g. 1 year), and start and end dates of the lease period.
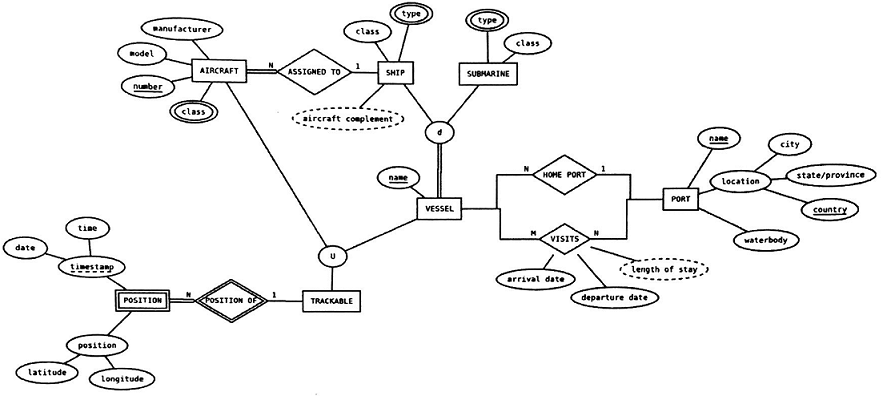
Q5. Convert the following ER diagram to a relational schema. For any case where you have a choice of ways to map a particular construct, choose the mapping that you think is best for this situation and explain your decision. Also be sure to specify all primary key and referential integrity (foreign key) constraints. If there are any aspects of the diagram that cannot be expressed in your relational schema, identify them and explain what the problem is.
Q6. Consider the following relation and functional dependencies for storing information about movies and actors:
MOVIE(title, year, length, genre, studio, president, rating, actor, role, birthdate, location)
- title, year → length, genre, studio, rating [title and year specify a movie]
- studio → president [a studio has one president]
- title, year, actor → role [actor plays one role in a movie]
- actor →birthdate, location ['actor' uniquely identifies an actor]
(a) What normal form is this relation in? Explain your answer.
(b) Apply normalization until you cannot decompose the relation(s) further. State the reasons behind each decomposition.
Q7. Convert the ER diagram from #1 to a relational schema. For any case where you have a choice of ways to map a particular construct, choose the mapping that you think is best for this situation and explain your decision. Also be sure to specify all primary key and referential integrity (foreign key) constraints. If there are any aspects of the diagram that cannot be expressed in your relational schema, identify them and explain what the problem is.
Q8. Consider the following relation and functional dependencies for storing race results:
RESULTS(name, location, date, racetype, time, class, course)
- name, location, date, course → time [one result per competitor, race, and course]
- location, date → racetype [location, date identifies the race]
- class → course [class determines the course]
Note that it is not the case that course → class i.e. multiple classes may be assigned to the same course.
(a) What normal form is this relation in? Explain your answer.
(b) Apply normalization until you cannot decompose the relation(s) further. State the reasons behind each decomposition. Can you fully satisfy all of the normal forms while maintaining the original constraints? Explain.