Potentiometer is a device mainly used to measure emf of a given cell and to compare emf's of cells. It is also used to calculate internal resistance of a given cell.
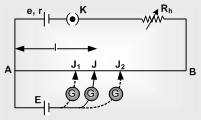
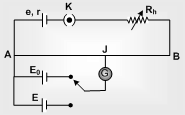
Circuit diagram: Potentiometer consists of a long resistive wire AB of length L (about 6 m to 10 m long) made up of constantan and a battery of known voltage e and internal resistance r called supplier battery or driver cell.
One terminal of another cell (whose emf E is to be measured) is connected at one end of the main circuit and the other terminal at any point on the resistive wire through a galvanometer G. That creates the secondary phase.
|
J = Jockey
K = Key
R = Resistance of potentiometer wire,
r = Given resistance of potentiometer wire.
Rh = Variable resistance which controls the current through the wire AB
(i) The specific resistance (r) of potentiometer wire must be high but its temperature coefficient of resistance (a) must be low.
|

|
(ii) All bigger potential terminals of primary and secondary circuits must be connected together at point A and all lower potential points must be connected to point B or jockey.
(iii) The magnitude of known potential difference must be greater than the value of unknown potential difference to be measured.
(iv) The potential gradient must remain fixed. For this the current in the initial circuit must remain constant and the jockey must not be slided in contact with the wire.
(v) The diameter of potentiometer line has to be uniform everywhere.
Potential gradient (x): Potential difference (or fall in potential) per unit length of wire is called potential gradient as.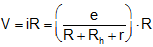 where .
where .
So 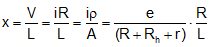
(i) Potential gradient directly relays upon
(a) The resistance per unit length (R/L) of potentiometer wire.
(b) The radius of potentiometer wire (i.e. Area of cross-section)
(c) The specific resistance of the material of potentiometer wire (i.e. r)
(d) The current goes through potentiometer wire
(ii) Potential gradient indirectly relays upon
(a) The emf of battery in the primary circuit (i.e. e)
(b) The resistance of rheostat in the primary circuit (i.e. Rh)
|
Working: Take a jockey is made to touch a point J on wire then potential difference between A and J will be V = xl
At that length (l) two energy difference are obtained
(i) V due to battery e and
(ii) E due to unknown cell
If V > E then current will flow in galvanometer circuit in one direction
|
|
If V < E then current will flow in galvanometer circuit in opposite direction 
If V = E then no current will flow in galvanometer circuit this condition to known as null deflection position, length l is known as balancing length.
In balanced condition E = xl
or 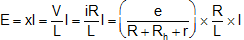
If V is constant then 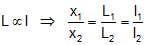
|
Standardization of Potentiometer: The phenomena of determining potential gradient experimentally are known as standardization of potentiometer.
Let the balancing size for the standard emf E0 is l0 then by the principle of potentiometer Eo = xlo => x = Eo/lo
|
|
Sensitivity of potentiometer: A meter is said to be more sensitive, if it measures a small potential difference more accurately.
(i) The sensitivity of potentiometer is assessed by its potential gradient. The relativity is inversely proportional to the potential gradient.
(ii) In order to gain the sensitivity of potentiometer
(a) The resistance in initial circuit will have to be decreased.
(b) The length of potentiometer line wire will have to be increased so that the length may be measured more accuracy.
Difference between potentiometer and voltmeter
|
Voltmeter
|
Potentiometer
|
|
It's resistance is high but finite
|
It's resistance is infinite
|
|
It takes some current from source of emf
|
It does not draw any current from the source of unknown emf
|
|
The potential difference calculated by it is lesser than the actual potential difference
|
The potential difference measured by it is equal to actual potential difference
|
|
Its sensitivity is low
|
Its sensitivity is high
|
|
It is a versatile instrument
|
It measures only emf or potential difference
|
|
It is based on deflection method
|
It is based on zero deflection method
|
Email based Physics assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching physics expert for help with Potentiometer questions? Potentiometer topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Physics assignment help and physics homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Potentiometer related problems. We provide step by step Potentiometer question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Potentiometer topic under physics theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving physics queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours