Osmotic pressure (π)
The osmotic pressure of the solution at a specific temperature can be defined as the excess hydrostatic pressure that builds up when solution is separated from the solvent by the semi-permeable membrane. It is denoted by the symbol π.
or
The Osmotic pressure can be defined as the excess pressure which should be applied to the solution in order to prevent flow of the solvent into the solution through semi-permeable membrane.
or
The Osmotic pressure is cab be described as the excess pressure which should be applied to the given solution in order to increase its vapour pressure until it becomes equal to that of solution.
(i) The Measurements of osmotic pressure : Following are the methods which are used for the measurement of osmotic pressure,
(a) Pfeffer's method,
(b) The Morse and Frazer's method,
(c) The Berkeley and Hartley's method,
(d) Townsend's negative pressure method,
(e) The De Vries plasmolytic method.
(ii) Determination of the molecular mass of non-volatile solute from the osmotic pressure (π) : The osmotic pressure is the colligative property. For the given solvent the osmotic pressure depends only upon th molar concentration of the solute but does not depend upon the nature of solute. The following relation relates the osmotic pressure to number of moles of the solute,
According to Boyle Van't Hoff law (at conc. temperature)
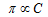 .....(i)
.....(i)
According to Gaylussac Van't Hoff law (at conc. tempemperature)
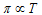 .....(ii)
.....(ii)
From equation (i) and (ii)
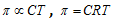 (Van't Hoff equation)
(Van't Hoff equation)
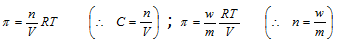
Where, C = concentration of solution in moles per litre
R = gas constant ; T = temperature
n = number of moles of solute ; V = volume of solution
m = molecular weight of solute ; w = weight of solute
(iii) The conditions for getting the accurate value of the molecular mass are,
(a) The solute must be non-volatile.
(b) The solution must be dilute.
(c) The solute must not undergo dissociation or association in the solution.
(iv) Relation of osmotic pressure with different colligative properties : Osmotic pressure is related to relative lowering of elevation of boiling point, vapour pressure, and the depression of freezing point according to the following relations,
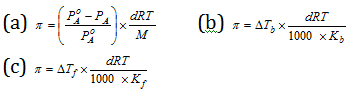
In the above relations given above,
p = Osmotic pressure;
d = Density of solution at temperature T;
R = Universal gas constant;
M= Mol. Mass of solute;
Kb= Molal elevation constant of the solvent;
kf = Molal depression constant of the solvent
(v) Isotonic, Hypertonic and Hypotonic solutions
(a) The isotonic or iso-osmotic solutions: The two solutions of different substances possessing same osmotic pressure at the same temperature are termed as isotonic solutions.
For the isotonic solutions, ∏1 = ∏2 Primary Condition .....(i)
Also, 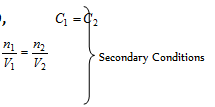
or 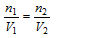
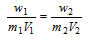 .....(ii)
.....(ii)
Eq. (ii) holds good only for those solutes which neither have the tendency to get associated nor dissociated in solution, examples are given below
Urea and glucose are isotonic then π1 = π2, C1 = C2
Urea and NaCl are isotonic then, π1 = π2, but C1 ≠ C2
(dissociate)
Urea and Benzoic Acid are isotonic then, π1 = π2, but C1 ≠ C2
(Associate)
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Osmotic Pressure questions? Osmotic Pressure topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Osmotic Pressure related problems. We provide step by step Osmotic Pressure question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Osmotic Pressure topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours