Application of superposition theorem
Consider an illustration to understand the application of superposition theorem.
Example:
The network is as shown in figure below. Compute Iab and Vcg by the help of superposition theorem.
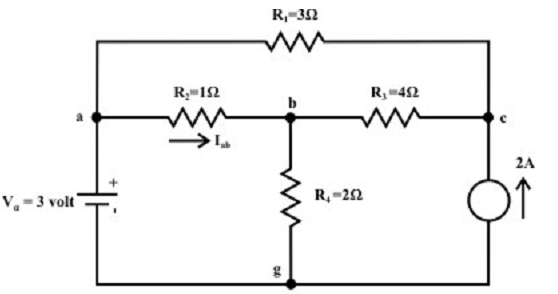
Solution:
Voltage Source Only (maintain one source at a time):
At first consider the voltage source Va which acts only in the circuit and the current source is substituted by its internal resistance (that is, in this condition internal resistance is unlimited
(∞ )). The analogous circuit diagram is as shown in figure below and computes the current flowing via the ‘a-b’ branch.
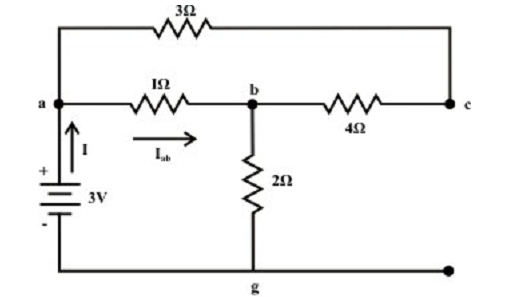
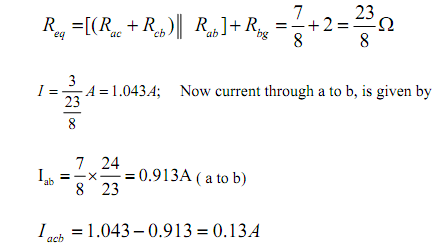
Now, voltage across c-g terminal:
Vcg = Vbg + Vcb = 2 x 1.043 + 4 x 0.13 = 2.61 volts
(Note: we are moving reverse to the direction of current flow and this point out that there is increase in potential). Note that ‘c’ is the higher potential than ‘g ’.
Current source only (retain one source at a time):
Let’s consider the current source Is =2A only and the voltage source Va is substituted by its internal resistance that is zero in the current situation. The analogous the simplified circuit diagram is shown below.
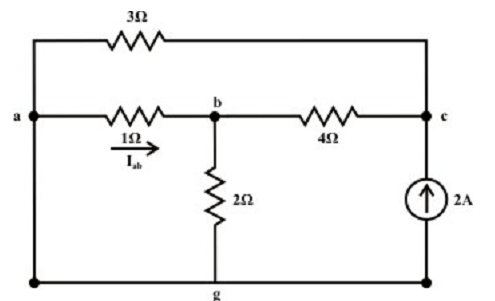
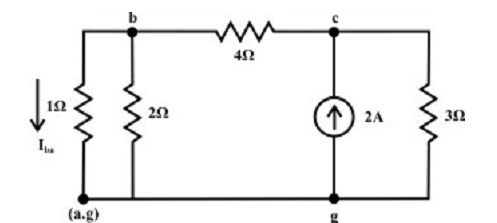
Current in the branches are as follows:
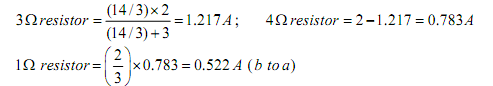
The voltage across 3Ω resistor (c & g terminals) Vcg = 1.217 x 3 = 3.651 volts
The total current flowing via 1Ω resistor (due to both sources) from a to b = 0.913 (due to voltage source merely; the current flowing from ‘a’ to ‘b ’) – 0.522 (due to current source only; the current flowing from ‘b ’to ‘a’) = 0.391A.
Total voltage across the current source Vcg = 2.61 volt + 3.65 = 6.26 volt.