THEORY OF INTER-TEMPORAL CONSUMPTION:
In the previous two units, we have been concerned with choices among contemporaneous commodities. An important class of choices made by consumers, however, relates to consumption over time, that is, how one allocates income earned in different time periods to consumption. It seems that when income is earned in an uneven pattern, individuals attempt to "smooth out" their consumption through borrowing and lending. In this way, people's consumption varies less than their income.
We began this discussion by considering consumption in just two-time period. Denote the present as period 1 and the future (next year) as period 2, and consumption in period 1 and 2 as x1 and x2. Suppose a person earns x10 in the present (this year) and x20 in the future (next year). Suppose also that this individual can borrow and lend in the "capital market" at rate of interest r. What this means is any income y not spent this year can be loaned to others, in return for which the consumer receives some greater amount y + r y = y(1 + r) next year. Alternatively, the consumer can increase present consumption by some amount y and repay y (1 + r) next year. The opportunity cost of consuming income y this year is thus forgoing consumption of y (1 + r) next year.
The price of present consumption is thus (1 + r) units of future consumption; alternatively, the price of future consumption is (1 / (1 + r)) units of present consumption. We commonly say that the present value of Rs. Y one year from now is Rs. y / (1 + r); this is merely the quantity, y, times its price in terms of present consumption. The interest rate is the "premium for earlier availability of goods". Wealth, W, in the present, is defined as the present value of current and future income. The consumer's budget constraint is that she cannot spend more than her wealth, i.e.,
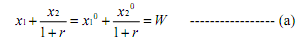
the consumer maximises U (x1x2) subject to equation(a)
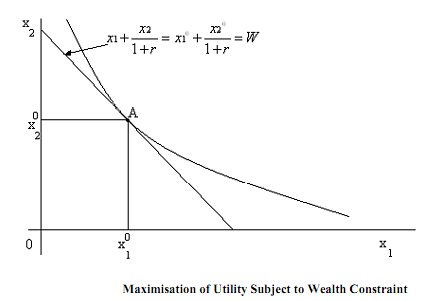
Though we are using "income" and "consumption" interchangeably as arguments in the utility function, it is well to remember, as pointed out by economist I. Fisher, that "income" really consists of consuming something. "Saving" (or dissaving) is just a way of rearranging consumption over time. Income is realised when it is consumed. The model is depicted in Figure The budget line has slope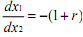 , the price of x1 in terms of x2, and passes through the endowment point A, (x10, x20). An increase in the interest rate represents an increase in the price of the present consumption, and has the effect of rotating the wealth constraint clockwise through A.
, the price of x1 in terms of x2, and passes through the endowment point A, (x10, x20). An increase in the interest rate represents an increase in the price of the present consumption, and has the effect of rotating the wealth constraint clockwise through A.