SOIL TEXTURE AND STRUCTURE
We have seen that soils are predominantly composed of particles of various sizes derived from the disintegration or decomposition of parent rock material. These particles that we see today may have been produced in early geologic period and they continue to be produced even today and moved by agents like wind, water or ice over considerable distances.
In this section, we shall discuss various textural classes and structures of soil. Soil texture refers to the relative particle-size composition of the soil. The particle size composition of a soil is the percentage of the mineral matter by weight in each fraction. In a given sample of soil, there may be present different sized particles in various proportions. Depending on their size (in diameter) the International Society of Soil Science has given specific nomenclature to the various panicle size classes which are as follows.
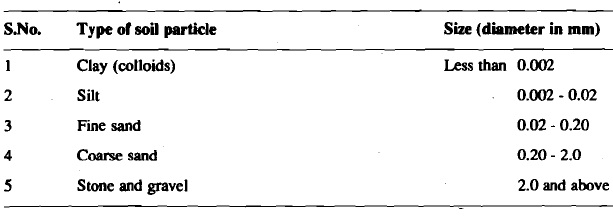
Soil mineral particles smaller than 0.002 mm are colloidal in nature and are called clay (see Table above). They do not settle quickly when mixed with water, as they form a colloidal solution or sol. The clay fraction or the-soil is most active physiochemically.
You have seen that based on the size, the soil particles are grouped into five categories. A soil may not necessarily be made up of one type of particles, that is, it mey contain particles belonging to any of these categories, in varying amounts. Depending on the proportion of
silt, clay and sand that the soil contains, the soils may be grouped into a number of classes such as sand, sandy loam, clay loam, clay etc.
All possible combinations of sand, silt and clay are condensed into twelve major soil classes. The class to which a soil belongs can be closely approximated by examination in the field but for accurate determination, mechanical analysis IS carned out to tind out relative amounts of particles of different sizes. The soil is assigned to a particular textural class after studying its mechanical analysis fraction. An experienced field surveyor can grade soils into these classes simply by feeling the soil when wet, between his fingers. The term soil texture refers to different proportions of sand, silt and clay in a soil but the arrangement or the state of aggregation of the soil particles in soil mass is referred to as soil structure. The aggregation of sand, silt, clay into compound particles may be of (i) granular, (ii) crumb, (iii) platy, (iv) blocky, (v) subangular blocky, (vi) prismatic and (vii) columnar nature.
The aggregation of soil particles is brought about by the colloidal fractions including sticky material of organic origin and very thin film of water molecules. Soil aggregates are called peds. The study of soil structure is important as it influences various physical properties of soil particularly aeration and water holding capacity.