RAW and WAW - Data hazards:
RAW (read after write) - j tries to read a source before i writes it, hence j wrongly gets the old value .This is the most usual type of hazard and the kind that we use forwarding to solve it.
WAW (write after write) - j tries to write an operand before i. The writes end up being performed in the incorrect order, leaving the value written by i rather than the value written by j in the destination. This hazard is there only in pipelines that write in more than 1 pipe stage or permit an instruction to proceed even when a preceding instruction is stalled. DLX integer pipeline writes a register just in WB and ignores this class of hazards.
WAW hazards would be possible if we perform the following 2 changes to the DLX pipeline:1)move write back for an ALU operation into the MEM stage, while the data value is available by then. Assume that the data memory access took 2 pipe stages.
Here is a sequence of 2 instructions which showing the execution in this revised pipeline, importance the pipe stage that writes the consequence:
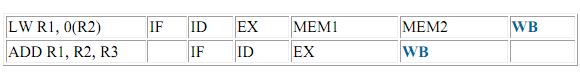
Unless this type of hazard is ignored, execution of this sequence on this revised pipeline will leave the result of the first write (the LW) in R1, before the result of the instruction ADD.
Let writes in different pipe stages introduces other problems, since 2 instructions may try to write at the similar clock cycle. DLX FP pipeline, which has both writes in different pipeline lengths and different stages and will deal with both write conflicts and WAW hazards in detail.