Message passing is probably the most extensively used parallel programming paradigm today. It is the mainly natural, portable and efficient approach for distributed memory systems. It gives natural synchronization between the processes so that explicit synchronization of Parallel Programming & Parallel Algorithms memory access is redundant. The programmer is dependable for determining all parallelism. In this programming model, multiple processes across the arbitrary number of machines, each with its own local memory, replace data through send and receive communication among processes. This model can be best understood by the diagram shown in Figure:
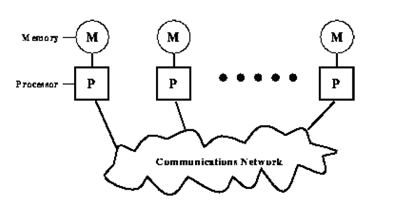
Message passage model
As the diagram specify, each processor has its own local memory. Processors perform computations with the data in their own memories and interact with the other processors, as and when needed, by communication network using message-passing libraries. The messages have the data being sent. But data is not only the constituent of the message. The other components in the message are:
- The address / identity of the processor that sending the message;
- Initial address of the data on the sending processor;
- The type of data being sent;
- The size of data;
- The address / identity of processor(s) are receiving the message, and
- Initial address of storage for the data on the receiving processor.
Once the message has been produced it is sent by the communication network. The communication can be in the following two forms:
i) Point-to-point Communication
The easiest form of message is a point-to- point communication and message is sent from the sending processor to a receiving processor. Message passing in point-to-point communication can be in two modes: synchronous and asynchronous. In synchronous transfer mode, the next message is sent only after the acknowledgement of delivery of the last message. In this mode the series of the messages is maintained. In asynchronous transfer mode, no acknowledgement for delivery is needed.
ii) Collective Communications
Some message-passing systems allow communication involving more than two processors. This type of communication may be called collective communication. Collective communication can be in one of these modes:
Barrier: In this mode no real transfer of data takes place unless all the processors involved in the communication implement a particular block, called barrier block, in their message passing program.
Broadcast: Broadcasting may be one-to-all or all-to-all. In one-to-all broadcasting, one processor sends the similar message to numerous destinations with a one operation whereas in all-to-all broadcasting, communication takes place in many-to-many fashion. The messages might be personalised or non-personalized. In a personalized broadcasting, unique messages are being sent to each destination processor.
Reduction: In this, one member of the group takes data from the other members, decreases them to a one data item which is usually made available to all of the participating processors.