Indirect Utility Functions:
Let qi denotes commodity i and pi is the price of that commodity. Let y denotes money income of the consumer. Suppose vi = pi/y. The budget constraint now may be written as
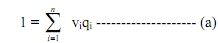
Since optimal solutions in the demand functions are homogeneous of degree zero in income and prices, nothing essential is lost by this transformation to "normalised" prices. The utility function U = f (q1, qn) together with equation (a) gives the following first order conditions of utility maximisation:

It gives the maximum utility as a function of normalised prices. The direct utility function describes preferences independent of market phenomena. The indirect utility function reflects a degree of optimisation and market prices. Applying the composite function rule of calculus to equation (c), we get
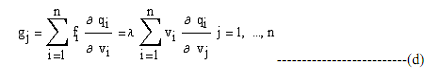
where the second equalities are based on equation (b). Partial differentiation of equation (a) with respect to vj yields

which is called the Roy's identity. Optimal commodity demands are related to the derivatives of the indirect utility function and the optimal value of the Lagrange multiplier (i.e., the marginal utility of income). Substituting equation (e) into the last equation of equation (b) gives
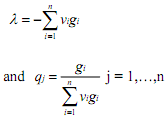
to provide an alternative form of Roy's identity. Now consider an optimisation problem in which equation (c) is minimised subject to equation (a) with normalised prices as variables and quantities as parameters. From the function, 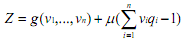 and setting its partials equal to zero, we get
and setting its partials equal to zero, we get
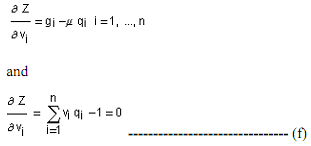
"Inverse demand functions" are obtained by solving equation (f) for the prices as functions of quantities:
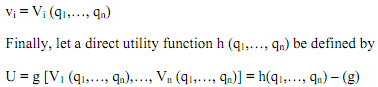
This provides a parallel to the direct problem in which quantities are variables and prices are parameters.