Using log(x1), log(x2) and log(x3) as the predictors, do pair wise scatterplots of all pairs of variables (including the response) and comment (use the pairs function). Do you think that multi collinearity might be a problem with these data?
Plot the ridge trace for a grid of 50 values for the shrinkage parameter � over the range [0; 1]. Based on this plot suggest a reasonable value for �. Find the estimates of the coe�cients for a ridge re gression with your chosen value of � (using centred and scaled predictors).
(The following question is based on Exercise 8.5 of Myers (1990), Classical and Modern Regression with Applications (Second Edition)," Duxbury).
With centred and scaled predictor variables, the ridge regression estimator for the coe�cients of the predictors is where y is the vector of responses, X is the design matrix for the centred and scaled predictors, is
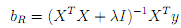
the shirnkage parameter and I denotes the identity matrix. We write n for the number of observations and k for the number of predictors. Writing biR for the ith component of bR, we will prove in this question that where �2 is the variance of the responses, and v�i, i = 1,.......k are the eigenvalues of XTX. The di�erent parts of the question below lead you through the proof.
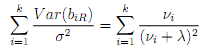
(a) Write XTX = QDQT for the eigenvalue decomposition of XTX, where D = diag(�v1,........v�k) is the diagonal matrix of eigenvalues and Q is an orthogonal matrix (QTQ = I) where the columns are the eigenvectors of XTX. Show that XTX +�I = Q(D+�I)QT .
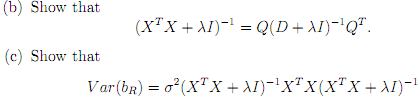
where V ar(bR) denotes the covariance matrix of bR. (Hint: recall the result from basic linear models that if Y is a k � 1 random vector with V ar(Y ) = V and if A is a k � k matrix and Z = AY then V ar(Z) = AV AT ).